Growth differentiation factor 11 attenuates sepsis-associated acute kidney injury by reducing inflammation and coagulation via PGC-1α/Nrf2 activation
- PMID: 40877798
- PMCID: PMC12392574
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-025-00762-2
Growth differentiation factor 11 attenuates sepsis-associated acute kidney injury by reducing inflammation and coagulation via PGC-1α/Nrf2 activation
Abstract
Background: Patients with sepsis commonly endure severe renal dysfunction and damage, hastening to end-stage renal failure with high mortality, and effective treatment options are currently lacking. Growth differentiation factor 11 (GDF11), belonging to the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) superfamily, has shown therapeutic potential for numerous acute and chronic inflammatory conditions. Nevertheless, its function in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury (SAKI) remains unclear.
Purpose: This study sought to explore GDF11's role in SAKI and determine the signaling pathways it modulates.
Methods: Alterations in GDF11 expression in the kidneys of mice with SAKI were analyzed. The influence of GDF11 knockdown and recombinant GDF11 (rGDF11) supplementation on cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced SAKI in mice was determined. RNA sequencing, Western blot, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), and kit assays were performed to explore the underlying mechanisms.
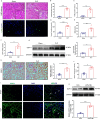
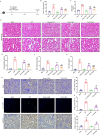
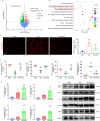
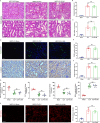
Results: Tubular epithelial cells and macrophages in the kidneys of CLP-induced SAKI mice exhibited high levels of GDF11 expression. Moreover, gene silencing of GDF11 using adeno-associated virus (AAV) aggravated renal dysfunction, increased tubular damage, and augmented renal apoptosis in CLP-induced SAKI mice. In contrast, replenishment of rGDF11 significantly mitigated these adverse effects. Further studies indicated that GDF11 stimulated the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)-regulated antioxidative pathways, primarily by inducing the expression of Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α), which subsequently decreased excessive inflammation and coagulation. Additionally, these beneficial effects of GDF11 were largely diminished by AAV-mediated PGC-1α knockdown and depletion of Nrf2 in CLP-induced SAKI mice.
Conclusions: In summary, these findings indicate that GDF11 is a potential therapeutic approach for SAKI and highlight the crucial role of PGC-1α/Nrf2 signaling in GDF11-mediated renal protection during SAKI.
Keywords: Antioxidation; Coagulation; Inflammation; Nrf2; Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Animal experiments were approved and reviewed by the Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University (approval no. WYYY-AEC-2022-0420, 10 August 2022). The Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University adheres to the principles and guidelines set forth by the International Council for Laboratory Animal Science (ICLAS), ensuring that our animal research meets international ethical standards. Consent for publication: The authors declare that they have no competing interests. All authors agree with the publication of this article. Competing interests: The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Cecconi M, Evans L, Levy M, Rhodes A. Sepsis and septic shock. Lancet. 2018;392(10141):75–87. - PubMed
-
- Skube SJ, Katz SA, Chipman JG, Tignanelli CJ. Acute kidney injury and sepsis. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2018;19(2):216–24. - PubMed
-
- White KC, Serpa-Neto A, Hurford R, Clement P, Laupland KB, See E, et al. Sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit: incidence, patient characteristics, timing, trajectory, treatment, and associated outcomes. A multicenter, observational study. Intensive Care Med. 2023;49(9):1079–89. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

