Effect of radical resection of lung cancer combined with breathing training on lung cancer patients in thoracic surgery: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 40877852
- PMCID: PMC12392598
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-025-03819-2
Effect of radical resection of lung cancer combined with breathing training on lung cancer patients in thoracic surgery: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Its objective was to use meta-analysis (MA) to methodically assess the impact of perioperative breathing exercises on the postoperative rehabilitation of patients with lung cancer (LC) having radical resection. METHODS: PubMed, and other databases were searched for randomized controlled trials on radical resection of LC combined with perioperative respiratory training from January 1995 to January 2024. After quality assessment, MA was performed using Review Manager 5.3 software.
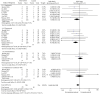
Results: A total of 14 studies involving 880 patients were included, of which 434 patients received perioperative breathing training (Intervention group, IG). The differences between the two groups in terms of MIP (MD = -13.31, 95% CI: [-24.43, -2.19]; Z = 2.35, P = 0.02), FVC (MD = -0.23, 95% CI = [-0.36, -0.11]; Z = 3.69, P = 0.0002), 6-minute walk test (6MWT) values (MD = 36.42, 95% CI: [4.37, 68.48]; Z = 2.23, P = 0.03), incidence of pneumonia (OR = 0.38, 95% CI = 0.20-0.72; Z = 2.95, P = 0.003), and complication rates (OR = 0.66, 95% CI = 0.46-0.94; Z = 2.29, P = 0.02) were statistically significant. However, there were no significant differences between the two groups in MEP (MD = -6.10, 95% CI: [-12.10, -0.11]; Z = 2.00, P = 0.05), FEV1 (MD = -0.25, 95% CI = [-0.58, 0.08]; Z = 1.47, P = 0.14), FEV1/FVC (MD = -3.78, 95% CI = [-7.65, 0.09]; Z = 1.91, P = 0.06), PEF (MD = -15.02, 95% CI = [-45.88, 15.83]; Z = 0.95, P = 0.34), atelectasis (OR = 0.52, 95% CI = 0.24-1.12; Z = 1.68, P = 0.09), pneumothorax (OR = 1.20, 95% CI = 0.63-2.29; Z = 0.57, P = 0.57), and mechanical ventilation incidence (OR = 0.99, 95% CI = 0.34-2.91; Z = 0.01, P = 0.99).
Conclusion: This MA demonstrates that perioperative respiratory training significantly improves MIP, FVC, and 6MWT in patients undergoing radical LC surgery, while effectively reducing the incidence of postoperative pneumonia and overall complications. However, its impact on MEP, certain pulmonary function parameters (FEV1, FEV1/FVC, PEF), and specific complications (atelectasis, pneumothorax, mechanical ventilation requirement) did not reach statistical significance. The findings support the inclusion of respiratory training in perioperative rehabilitation programs for LC patients to optimize postoperative recovery outcomes.
Keywords: Breathing training; Lung function; MA; Postoperative pulmonary complications; RMS; Radical resection of LC.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

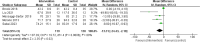
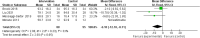



Similar articles
-
Preoperative exercise training for patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 7;6(6):CD012020. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012020.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 28;9:CD012020. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012020.pub3. PMID: 28589547 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Non-invasive positive pressure ventilation for prevention of complications after pulmonary resection in lung cancer patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 25;(9):CD010355. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010355.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 06;3:CD010355. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010355.pub3. PMID: 26407182 Updated.
-
Preoperative physical therapy for elective cardiac surgery patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Nov 14;11(11):CD010118. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010118.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 23152283 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary rehabilitation for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Feb 23;2015(2):CD003793. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003793.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25705944 Free PMC article.
-
Inspiratory muscle training, with or without concomitant pulmonary rehabilitation, for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 6;1(1):CD013778. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013778.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36606682 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu H. Effect of traditional medicine on clinical cancer. Biomedical J Sci Tech Res. 2020;30(4):23548–51.
-
- Duma N, Santana-Davila R, Molina JR. Non-Small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019;94(8):1623–40. - PubMed
-
- Jiménez-Tornero J, Cortés-Flores AO, Chávez-Tostado M, Morgan-Villela G, Del Zuloaga-Fernández C, Del Zuloaga-Fernández R, García-González LA, Fernández-Avalos VS, Miranda-Ackerman RC, Alvarez-Villaseñor AS, Ambriz-González G, Barbosa-Camacho FJ, Fuentes-Orozco C, Contreras-Cordero VS, González-Ojeda A. Effect of a preoperative single-dose steroid on pulmonary function and postoperative symptoms after modified radical mastectomy: results of a randomized clinical trial. Gland Surg. 2020;9(5):1313–27. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baumeister SE, Baurecht H, Nolde M, Alayash Z, Gläser S, Johansson M, Amos CI, International Lung Cancer Consortium, Johnson EC, Hung RJ. Cannabis use, pulmonary function, and lung cancer susceptibility: a Mendelian randomization study. J Thorac Oncol. 2021;16(7):1127–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

