Integrin signaling pathways in mesenchymal stem cells
- PMID: 40877985
- PMCID: PMC12395929
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-025-04608-8
Integrin signaling pathways in mesenchymal stem cells
Abstract
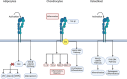
This review provides an overview of the integrin signaling pathways and their roles in mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into adipocytes, chondrocytes, and osteoblasts. In these three differentiated cells, the cell extracellular matrix plays an important role in regulating the integrin signaling pathway, as the presence of growth factors and other molecules in the extracellular matrix will affect the cell differentiation. The focus of this review is to elucidate the role of the integrin signaling pathway in adipogenesis, chondrogenesis, and osteogenesis, highlighting its diverse contributions to tissue homeostasis and repair. By synthesizing current knowledge, this paper aims to inspire further research into the therapeutic potential of targeting integrin pathways in stem cell-based tissue engineering.
Keywords: Cell differentiation; Cell signalling; Cell-ECM interactions; Extracellular matrix (ECM); Integrin signalling pathway; Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bentmann A, Kawelke N, Moss D, Zentgraf H, Bala Y, Berger I, et al. Circulating fibronectin affects bone matrix, whereas osteoblast fibronectin modulates osteoblast function. J Bone Miner Res. 2010;25(4):706–15. 10.1359/jbmr.091011. - PubMed
-
- Bonewald LF. Osteocytes. Marcus Feldman’s Osteoporosis. 2021;1:135–63.
-
- Brunner M, Jurdic P, Tuckerman JP, Block MR, Bouvard D. New insights into adhesion signaling in bone formation. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2013;1(305):1–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

