Characterizing Stroke Clots Using Single-Cell Sequencing
- PMID: 40878981
- PMCID: PMC12553457
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.125.041738
Characterizing Stroke Clots Using Single-Cell Sequencing
Abstract
Background: Ischemic stroke results in significant morbidity and mortality. By examining gene expression of cells comprising stroke clots, we aim to gain valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of this disease and identify potential biomarkers of stroke cause.
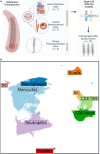
Methods: We employed single-cell RNA sequencing to analyze 10 clot samples from patients diagnosed with large vessel occlusion stroke. We aimed to identify and compare the immune cell compositions and gene expression profiles between stroke clots (atrial fibrillation vs carotid atherosclerosis). We also used Multi-marker Analysis of Genomic Annotation and genome-wide association studies summary statistics from the GIGASTROKE consortium to assess associations between genetic variants and cell type-specific gene expression within the stroke subtypes.
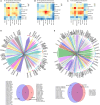
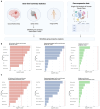
Results: Our analysis revealed distinct immune cell populations, including monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, neutrophils, and T cells in both clot types. Notably, we observed significant differences in gene expression within the mononuclear phagocytic system cells between clots from patients with atrial fibrillation and carotid atherosclerosis. We identified specific genes associated with atherosclerosis and stroke-related processes, such as CD74, HLA-DRB1*01, HTRA1, C1Q, CD81, and CR1 from patients with carotid atherosclerosis. In atrial fibrillation clots, CD8 T cells and natural killer cells show upregulated expression of genes such as GZMH, GZMB, S100A4, FCGBP2, HLA-A, TIMP1, CLIC1, and IFITM2, indicating their involvement in cytotoxic activities and potential tissue damage. The Multi-marker Analysis of Genomic Annotation approach highlighted significant genetic associations within leukocytes underscoring the potential roles of B cells, T cells, and macrophages in clot pathogenesis.
Conclusions: This study illuminates the immune and transcriptomic landscape within clots, offering potential biomarkers and lays the foundation for future research.
Keywords: immune cell profiling; single‐cell RNA sequencing; stroke cause.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Matouk is a consultant for Penumbra, Terumo Neurovascular, and Boston Scientific.
Figures


References
-
- Tsao CW, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, Anderson CAM, Arora P, Avery CL, Baker‐Smith CM, Beaton AZ, Boehme AK, Buxton AE, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2023 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2023;147:e93–e621. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001123 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sporns PB, Jeibmann A, Minnerup J, Broocks G, Nawabi J, Schön G, Fiehler J, Wildgruber M, Heindel W, Kemmling A, et al. Histological clot composition is associated with Preinterventional clot migration in acute stroke patients. Stroke. 2019;50:2065–2071. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.023314 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

