Medication Adherence Technologies: A Classification Taxonomy Based on Features
- PMID: 40881105
- PMCID: PMC12381639
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpdig.2025.100237
Medication Adherence Technologies: A Classification Taxonomy Based on Features
Abstract
Objective: To develop a comprehensive classification system for medication adherence technologies based on an inventory of characteristics and features of existing technology.
Participants and methods: Using a 3-stage approach methodology-development, validation, and evaluation, the study adopted the taxonomy development method and was conducted from February 1, 2023 to July 31, 2024. In the development stage, medication adherence technologies were defined, end users were identified, and a meta-characteristic was determined; using both empirical-to-conceptual and conceptual-to-empirical approaches, dimensions and characteristics were identified. The taxonomy was validated through the Delphi consensus approach and classifying 20 sample medication adherence technologies and evaluated by mapping to codes identified from a qualitative study.
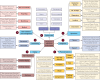
Results: After undergoing 8 iterations, which included incorporating feedback from a Delphi consensus survey, the final taxonomy comprised 7 dimensions, 25 subdimensions, and 320 characteristics. These key dimensions include Physical Features, Display, Connectivity, System Alert, Data Collection and Management, Operations, and Integration. The taxonomy was considered complete and valuable once all preestablished ending conditions were met, and its applicability and comprehensiveness were verified by comparing various medication adherence technologies and mapping to codes identified from a qualitative study.
Conclusion: This study successfully establishes the first comprehensive classification system for medication adherence technologies based on features, addressing a critical gap in literature. The taxonomy provides a structured framework for categorizing and evaluating technologies, supporting usability testing and the selection of appropriate devices tailored to the unique needs of older adults.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Patel reports grants from National Research Council (NRC), Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Jones Healthcare Group, and Catalyst Health; travel support from National Research Council (NRC) and Canadian Institutes of Health Research; and contribution of medical adherence technology from Jones Healthcare Group and Catalyst Health. The other authors report no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World population prospects 2022: ten key messages United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. https://population.un.org/wpp/
-
- World report on ageing and health World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous