Bombesin Receptor Subtype-3 Regulates Tumor Growth by HER2 Tyrosine Phosphorylation in a Reactive Oxygen Species-Dependent Manner in Lung Cancer Cells
- PMID: 40881937
- PMCID: PMC12383237
- DOI: 10.3390/targets3010007
Bombesin Receptor Subtype-3 Regulates Tumor Growth by HER2 Tyrosine Phosphorylation in a Reactive Oxygen Species-Dependent Manner in Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
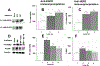
Bombesin receptor subtype-3 (BRS-3) is a type 1 G-protein-coupled receptor. BRS-3 is an orphan GPCR which is structurally related to the neuromedin B and gastrin-releasing peptide receptors. When activated, BRS-3 causes phosphatidylinositol turnover in lung cancer cells. BRS-3 stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of the epidermal growth-factor receptor (ErbB1), however it is unknown if it transactivates ErbB2/HER2. Adding the nonpeptide BRS-3 allosteric-agonist, MK-5046 or the peptide agonist, BA1 to the lung cancer cell line, NCI-H727 or BRS-3-transfected NCI-H1299 lung cancer cells, increased tyrosine phosphorylation of HER2/ERK2. This increase was antagonized by the BRS-3 peptide antagonist, Bantag-1 and the small molecule BRS-3 antagonist, ML-18. The increase in HER2/ERK phosphorylation caused by MK-5046 was inhibited by ROS inhibitors, N-acetylcysteine and Tiron (superoxide-scavenger). Adding MK-5046 to lung cancer cells increased reactive-oxygen species which was inhibited by NAC or Tiron. MK-5024 and BA1 increased NSCLC colony formation whereas, Bantag-1/ML-18 inhibited proliferation. These results indicate that in lung cancer cells activation of BRS-3 regulates HER2-transactivation in ROS-dependent manner which can mediate tumor growth. These results raise the possibility that the use of HER2-inhibiting compounds alone or in combination with other agents, could be a novel approach in the treatment of these tumors.
Keywords: BRS-3; HER2; ROS; lung cancer; proliferation μ; transactivation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



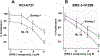
Similar articles
-
Bombesin receptor subtype-3 agonists stimulate the growth of lung cancer cells and increase EGF receptor tyrosine phosphorylation.Peptides. 2011 Aug;32(8):1677-84. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2011.06.011. Epub 2011 Jun 25. Peptides. 2011. PMID: 21712056 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ML-18 is a non-peptide bombesin receptor subtype-3 antagonist which inhibits lung cancer growth.Peptides. 2015 Feb;64:55-61. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2014.12.005. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Peptides. 2015. PMID: 25554218 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
References
-
- Fathi Z; Corjay MH; Shapira H; Wada E; Benya R et al. BRS-3: novel bombesin receptor subtype selectively expressed in testis and lung carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem 1993, 268(8), 5979–5984. - PubMed
-
- Li M; Liang P; Liu D; Yuan F; Chen GC et al. Bombesin Receptor Subtype-3 in Human Diseases. Arch. Med. Res 2019, 50, 463–467. - PubMed
-
- Mantey SA; Weber HC; Sainz E; Akeson M; Ryan RR et al. Discovery of a high affinity radioligand for the human orphan receptor, bombesin receptor subtype 3, which demonstrates it has a unique pharmacology compared to other mammalian bombesin receptors. J. Biol. Chem 1997, 272(41), 26062–26071. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
