Proanthocyanidins inhibit CYP1B1 through mixed-type kinetics and stable binding in molecular dynamics simulations
- PMID: 40883330
- PMCID: PMC12397248
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-12781-2
Proanthocyanidins inhibit CYP1B1 through mixed-type kinetics and stable binding in molecular dynamics simulations
Abstract
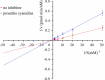
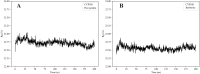
Cytochrome P450 1B1 (CYP1B1) is a heme-containing enzyme involved in procarcinogen activation and estrogen metabolism, contributing to tumor progression. This study investigates the inhibitory effects of proanthocyanidin (PA) on CYP1B1-catalyzed reactions and its underlying mechanisms. Enzyme kinetics revealed that PA exerts mixed-type inhibition with an IC₅₀ of 2.53 ± 0.01 μM. Molecular docking demonstrated that PA binds to key residues (Phe231, Gly329, Ala330, Asn228, Asn265) and the heme cofactor through hydrogen bonding and π-π stacking, interfering with substrate binding and electron transfer. Molecular dynamics simulations over 200 ns confirmed the stability of the PA-CYP1B1 complex. To validate the stability and inhibitory relevance of the simulation results, berberine, a known CYP1B1 inhibitor, was used as a positive control in parallel analyses. In silico ADMET prediction indicated high intestinal absorption and a favorable safety profile, with no significant CYP inhibition or mutagenicity. However, low membrane permeability and multiple drug-likeness violations suggest limited oral bioavailability. These findings support the potential of PA as a natural CYP1B1 inhibitor for cancer prevention and treatment. Further structural optimization or formulation strategies may enhance its pharmacokinetic properties and clinical applicability.
Keywords: ADMET; CYP1B1; Inhibition kinetics; Molecular dynamics; Proanthocyanidin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

