Effect of GLP-1RA on coronary progression and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetic patients after PCI: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 40883386
- PMCID: PMC12397294
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-17574-1
Effect of GLP-1RA on coronary progression and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetic patients after PCI: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
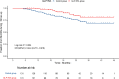
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) reduce incidence of cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetes (T2D) patients. Yet, the impact of GLP-1RAs on coronary lesion progression and cardiovascular outcomes after coronary stent implantation remains unclear. We aimed to investigate the effects of GLP-1RAs on coronary lesion progression and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). This prospective cohort study enrolled 1664 patients with T2D who underwent PCI from January 2020 to March 2024. Matched GLP-1RAs-treated and non-treated cohorts were formed using the propensity score matching method. The primary endpoint was the incidence of MACEs (cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, non-fatal stroke, hospitalization for heart failure). Secondary endpoints included in-stent restenosis and non-target lesion progression. Two 131-patient cohorts with balanced baseline characteristics were formed by propensity score matching. During the median follow-up period of 20 months (ranging from 6 to 48 months), the incidence of MACEs was significantly lower in the GLP-1RA group (7.63%)compared to the control group (19.85%) (HR 0.444; 95%CI, 0.215-0.918; P = 0.024). During a median follow-up period of 12 months, 79.39% (104/131) of patients in the control group and 82.44% (108/131) of patients in the GLP-1RA group successfully underwent coronary angiography follow-up. The incidence of in-stent restenosis was 2.78% (3/108) in the GLP-1RA group and 11.54% (12/104) in the control group (P = 0.028). Non-target lesion progression was found in 10.19% (11/108) patient of the GLP-1RA group and 22.12% (23/104) in the control group (P = 0.037). Notable disparities were observed between the two groups regarding improvements of BMI, SBP, HbA1c, LDL-C, CRP. GLP-1RAs significantly reduced the incidence of MACEs and coronary lesion progression in patients with T2D after coronary stent implantation. These findings suggest that GLP-1RAs may have beneficial effects on cardiovascular outcomes and coronary artery disease progression in this population.
Keywords: Coronary lesion progression; GLP-1RAs; Major adverse cardiovascular events; Percutaneous coronary intervention; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists are associated with fewer major adverse cardiovascular and limb events in patients with moderate peripheral arterial disease.J Vasc Surg. 2025 Sep;82(3):1024-1032.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2025.05.037. Epub 2025 Jun 6. J Vasc Surg. 2025. PMID: 40484062
-
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists for people with chronic kidney disease and diabetes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Feb 18;2(2):CD015849. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015849.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 39963952
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists and 13 Obesity-Associated Cancers in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Jul 1;7(7):e2421305. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.21305. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. PMID: 38967919 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose-Lowering Medications and Risk of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Exacerbations in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.JAMA Intern Med. 2025 Apr 1;185(4):399-410. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.7811. JAMA Intern Med. 2025. PMID: 39928303
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists and sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors for people with cardiovascular disease: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 25;10(10):CD013650. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013650.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34693515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sivakumar, P. M., Premkumar, B., Prabhawathi, V. & Prabhakar, P. K. Role of GLP-1 analogs in the management of diabetes and its secondary complication. Mini Rev. Med. Chem.21(20), 3166–3182. 10.2174/1389557521666210422114909 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Taha, M. B. et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: A medication for obesity management. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep.24(8), 643–654. 10.1007/s11883-022-01041-7 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 202402AA310073/Science and Technology Planning Project of Yunnan Province of China
- 82100462/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 202240149/Shanghai Municipal Health Commission
- JYLJ202209/Clinical Research Program of Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital
- SHDC12023123/the 15th Batch of Emerging Frontier Project Topics of Shanghai Shenkang
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous