Optimization of needle punched nonwoven filter media for enhanced dust filtration performance
- PMID: 40883521
- PMCID: PMC12397395
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-17543-8
Optimization of needle punched nonwoven filter media for enhanced dust filtration performance
Abstract
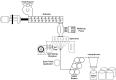
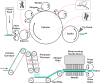
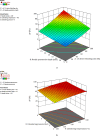
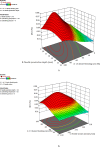
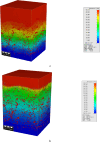
Nonwoven fabrics play a critical role in filtration applications due to their unique structural properties, including high porosity, irregular structure, and customizable fiber arrangements. These characteristics make them ideal for various filtration purposes, from industrial air filters to indoor air filters for HVAC and engine air filters for automobiles. To this end, polypropylene fibers were spun at two different finenesses (1.5 and 3 denier) using an industrial-scale melt-spinning machine. The nonwoven filter media were then fabricated based on an I-optimal design response surface methodology (RSM-I-optimal) method using a semi-industrial needle punching line. The process parameters considered include the blending ratio of 1.5 denier fibers (0-100%), needle penetration depth (9-16 mm), needling strokes (110-430 strokes/min), calendering temperature (120-140 °C), and calendering pressure (2-6 bar). The 3D microstructure of the samples was analyzed using X-ray µCT, and the morphology was examined through image analysis. Filtration performance, including efficiency, pressure drop, and quality factor, was characterized according to ISO 11,057. The influence of input variables on filtration performance was evaluated using ANOVA, leading to the development of quadratic models for predicting efficiency, pressure drop, and quality factor. The interaction effects of the process parameters were also studied. Optimal conditions were determined to maximize efficiency and quality factor while maintaining pressure drop below 70 Pa. Under these conditions, the predicted values of efficiency, pressure drop, and quality factor were 94.99%, 61.07 Pa, and 0.0456 1/Pa, respectively. Subsequently, four filter media were manufactured under optimal conditions, and their performance was assessed. The experimental results yielded efficiency, pressure drop, and quality factor of 93.37%, 62.52 Pa, and 0.0434 1/Pa, respectively. Additionally, a numerical dust loading simulation was performed through the realistic 3D structure of the optimized filter medium. The optimized filter exhibited good filtration performance in experiments, modeling, and CFD. This research demonstrates that by carefully optimizing process parameters, the filtration performance of needle punch nonwoven fabrics can be significantly enhanced, making them more effective for industrial filtration applications.
Keywords: Filtration performance; Microstructural properties, numerical simulation; Needled nonwoven fabric; Process parameters; RSM-I-optimal; X-ray micro-computed tomography.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Sexual Harassment and Prevention Training.2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Mar 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36508513 Free Books & Documents.
-
Electrophoresis.2025 Jul 14. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 14. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36251838 Free Books & Documents.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Search strategies to identify diagnostic accuracy studies in MEDLINE and EMBASE.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Sep 11;2013(9):MR000022. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000022.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24022476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liang, L., Wang, Z. & Li, J. The effect of urbanization on environmental pollution in rapidly developing urban agglomerations. J. Clean. Prod.237, 117649 (2019).
-
- Qi, G., Che, J. & Wang, Z. Differential effects of urbanization on air pollution: evidences from six air pollutants in Mainland China. Ecol. Ind.146, 109924 (2023).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

