Role of P38 lipoprotein in Mycoplasma penetrans adhesion to human urothelial cells
- PMID: 40885928
- PMCID: PMC12398969
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-025-04215-w
Role of P38 lipoprotein in Mycoplasma penetrans adhesion to human urothelial cells
Abstract
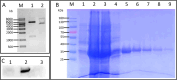
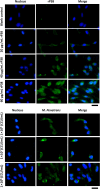
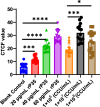
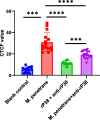
Mycoplasma penetrans, a bacterium detected in individuals seropositive for HIV and phylogenetically clustered with M. muris, may contribute to the progression of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS). Cellular adhesion is essential for Mycoplasma infection of host cells. M. penetrans exhibits the capacity to adhere to and invade human cells, precipitating diseases of the genital and urinary tracts. However, the proteinaceous mediators of its adhesion remain largely elusive. The P35 family lipoprotein, encoded by the mpl gene, is a prominent surface lipoprotein of M. penetrans. Here, we investigated the role of P38, a member of the P35 family, in the adhesion of M. penetrans to human urothelial cells (SV-HUC-1). We expressed and purified recombinant P38 (rP38) and confirmed its localization using Western blot. Adhesion assays, adhesion inhibition assays, and adhesion competition assays were performed to evaluate the adhesive properties of rP38 and M. penetrans. Our findings indicated that P38 localizes to the cell membrane of M. penetrans. Both rP38 and M. penetrans adhered to SV-HUC-1 cells, with optimal adhesion observed at 60 μg/mL for rP38 and 1 × 10⁷ CCU (Colony-Changing Units)/mL for M. penetrans. Anti-rP38 serum partially inhibited M. penetrans adhesion to SV-HUC-1 cells, and rP38 competed with M. penetrans for binding to SV-HUC-1 cells. These results suggest that P38 may function as an adhesin of M. penetrans, providing insights into its pathogenic mechanisms.
Keywords: Mycoplasma; Mycoplasma penetrans; Adhesion protein; Lipoprotein; P38.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The antibody preparation using animals was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of South China, and all animal procedures were conducted in accordance with the institutional regulations (No. 2023–38). Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Screening the receptors for Mycoplasma penetrans P35 lipoprotein and characterization of its functional binding domains.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Mar 17;15:1525789. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1525789. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40166371 Free PMC article.
-
MBOVJF4278_00820 encodes a novel cytoadhesin of Mycoplasma bovis binding to heparin.Infect Immun. 2025 May 13;93(5):e0060624. doi: 10.1128/iai.00606-24. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Infect Immun. 2025. PMID: 40265913 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Serum and urine nucleic acid screening tests for BK polyomavirus-associated nephropathy in kidney and kidney-pancreas transplant recipients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 28;11(11):CD014839. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014839.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39606952
-
Taxane monotherapy regimens for the treatment of recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 12;7(7):CD008766. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008766.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866378 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

