Intrathecal Antibody Synthesis in Autoimmune Nodopathy
- PMID: 40887769
- PMCID: PMC12399800
- DOI: 10.1111/jns.70057
Intrathecal Antibody Synthesis in Autoimmune Nodopathy
Abstract
Background: Autoimmune nodopathy (AN) is caused by autoantibodies targeting the nodes of Ranvier or paranodes. AN frequently affects cranial nerves and spinal nerve roots and may accompany central demyelination, all of which belong to the intrathecal compartment. We aimed to ascertain the frequency of intrathecal antibody synthesis and blood-CSF barrier (BCSFB) dysfunction in AN and their clinical correlates.
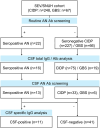
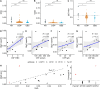
Methods: We analyzed paired cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum samples from 110 patients with AN, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP), and Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). BCSFB dysfunction and intrathecal total IgG synthesis were assessed using QAlb, QIgG-total, and IgG index. Flow cytometry was used to evaluate intrathecal autoantibody synthesis.
Results: Compared to CIDP and GBS, AN patients more frequently exhibited BCSFB dysfunction (87.5%) and intrathecal total IgG synthesis (68.8%). Among AN patients with cranial nerve or brain involvement (8/16, 50%), all had either an elevated IgG index (n = 7) or CSF-specific oligoclonal bands (n = 1). Intrathecal autoantibody synthesis was confirmed in 2 patients. Notably, both patients initially presented with cranial neuropathies. No CSF-restricted AN autoantibodies were found in the 39 seronegative CIDP and GBS patients.
Conclusions: AN exhibits distinct immunopathogenesis compared to CIDP and GBS. Intrathecal synthesis of total IgG is associated with cranial nerve or central nervous system involvement, while that of AN-specific autoantibodies relates to cranial nerve onset diseases.
Keywords: autoimmune nodopathy; blood‐CSF barrier; intrathecal antibody synthesis.
© 2025 The Author(s). Journal of the Peripheral Nervous System published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Peripheral Nerve Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Min Y. G., Ju W., and Sung J. J., “Superior Oblique Palsy as the Initial Manifestation of Anti‐Contactin‐1 IgG4 Autoimmune Nodopathy: A Case Report,” Journal of Neuroimmunology 391 (2024): 578348. - PubMed
-
- Mori Y., Yoshikura N., Fukami Y., et al., “Anti‐Contactin‐Associated Protein 1 Antibody‐Positive Nodopathy Presenting With Central Nervous System Symptoms,” Journal of Neuroimmunology 394 (2024): 578420. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

