Multi-cancer Detection Using Pattern Formation in Drying Body Fluids: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies
- PMID: 40888601
- PMCID: PMC12402661
- DOI: 10.1177/15330338251333994
Multi-cancer Detection Using Pattern Formation in Drying Body Fluids: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies
Abstract
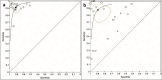
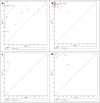
IntroductionThe ability to detect multiple cancer types with high sensitivity has the potential to reduce diagnostic delays and improve treatment outcomes. Diagnostic patterning tests (DPTs), which utilize self-organized patterns in drying body fluids, are a relatively unexplored diagnostic method. This systematic review and meta-analysis assessed their accuracy for multi-cancer detection.MethodsSearches were conducted in PubMed, Web of Science, eLibrary Russia, and other databases for studies evaluating DPT accuracy in cancer detection. Study quality was assessed using the QUADAS-2 tool. Data were analyzed for (i) untreated cancers, (ii) treated cancers, and (iii) precancerous conditions, with controls comprising (iv) healthy individuals and (v) non-cancer patients. Meta-analysis adhered to the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy.ResultsOf the 610 identified records, 41 studies involving 15,969 participants were included, encompassing 5265 cancer cases and 189 precancerous condition cases. Pooled sensitivity and specificity across all DPTs were 0.89 (95% CI, 0.83-0.93) and 0.90 (95% CI, 0.84-0.93), respectively. Copper chloride crystallization applied to blood demonstrated the highest sensitivity (0.93; 95% CI, 0.87-0.96) and specificity (0.93; 95% CI, 0.85-0.97), though differences between tests were not statistically significant.ConclusionDespite high heterogeneity and the potential risk of bias, DPTs showed a satisfactory degree of accuracy in detecting over 50 cancer types. Further research is needed to evaluate their potential for early cancer detection.
Keywords: copper chloride crystallization of blood; diagnostic tests; droplet evaporation; meta-analysis; multi-cancer detection; patterns in drying body fluids.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Are Artificial Intelligence Models Reliable for Clinical Application in Pediatric Fracture Detection on Radiographs? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Aug 20. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003660. Online ahead of print. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 40839831
-
Diagnostic test accuracy of nutritional tools used to identify undernutrition in patients with colorectal cancer: a systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 May 15;13(4):141-87. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1673. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447079
-
The diagnostic accuracy of the GenoType(®) MTBDRsl assay for the detection of resistance to second-line anti-tuberculosis drugs.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Oct 29;(10):CD010705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010705.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25353401 Free PMC article.
-
Regional cerebral blood flow single photon emission computed tomography for detection of Frontotemporal dementia in people with suspected dementia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jun 23;2015(6):CD010896. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010896.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26102272 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Promoting cancer early diagnosis. World Health Organization; 2022, Accessed 16 May 2022.
-
- GLOBOCAN. Estimated number of New Cases in 2020; International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2022. Accessed 16 May 2022.
-
- Zhou Y, Abel GA, Hamilton W, et al. Diagnosis of cancer as an emergency: A critical review of current evidence. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017;14(1):45‐56. - PubMed
-
- Klein EA, Richards D, Cohn A, et al. Clinical validation of a targeted methylation-based multi-cancer early detection test using an independent validation set. Ann Oncol. 2021;32(9):1167‐1177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

