MAP3K13-232aa encoded by circMAP3K13 enhances cisplatin-induced pyroptosis by directly binding to IKKα in gastric adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 40890114
- PMCID: PMC12402440
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-025-07991-5
MAP3K13-232aa encoded by circMAP3K13 enhances cisplatin-induced pyroptosis by directly binding to IKKα in gastric adenocarcinoma
Abstract
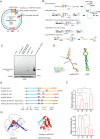
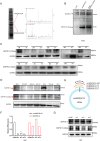
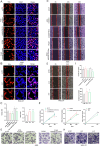
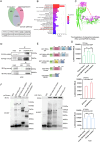
Gastric cancer (GC) is one of the most common and lethal malignancies in developing countries, with particularly high prevalence in China. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have garnered increasing attention for their roles in disease pathogenesis. While circRNAs can be translated, there have been few investigations into the biological functions of "translatable circRNAs" in the initiation and progression of gastric adenocarcinoma. In this study, we identified a circRNA, circMAP3K13, which inhibits the proliferation and migration of GC cells. CircMAP3K13 was found to encode a previously unreported 26 kDa protein, designated MAP3K13-232aa. Mechanistically, MAP3K13-232aa binds directly to the kinase domain of IKKα and enhances its activity, thereby promoting NF-κB signaling. This activation leads to upregulation of NLRP3 and increased cisplatin-induced pyroptosis in GC cells. Moreover, MAP3K13-232aa enhances pyroptosis and reduces tumorigenicity and metastasis in vivo. Taken together, both circMAP3K13 and its encoded protein MAP3K13-232aa represent potential therapeutic targets in GC.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Shenzhen University Health Science Center. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients. All methods in the study were performed in accordance with the guidelines of The First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University.
Figures



References
-
- Johnston FM, Beckman M. Updates on management of gastric cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019;21:67. - PubMed
-
- Hsu MT, Cocaprados M. Electron-microscopic evidence for the circular form of RNA in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1979;280:339–40. - PubMed
-
- Altesha MA, Ni T, Khan A, Liu K, Zheng X. Circular RNA in cardiovascular disease. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234:5588–5600. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

