Kueselia aquadivae gen. nov., sp. nov., the first member of the family Isosphaeraceae isolated from subsurface percolates
- PMID: 40890241
- PMCID: PMC12402505
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-17081-3
Kueselia aquadivae gen. nov., sp. nov., the first member of the family Isosphaeraceae isolated from subsurface percolates
Abstract
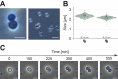
Subsurface habitats, found under various geological conditions, exhibit diverse microbial communities. The vadose zone, a previously unexplored subsurface compartment, connects the surface to phreatic groundwater. Drilling into the subsurface allows access to these habitats for microbial diversity study. Due to nutrient limitation, subsurface microbiomes adapt, potentially producing biotechnologically important biomolecules. Planctomycetota, known for possessing about 20 to 45% of protein-coding genes of unknown function, may be relevant in this context. A percolate water sample from the weathered bedrock of the Hainich Critical Zone Exploratory (CZE; Thuringia, Germany) was processed to enrich planctomycetes, leading to the isolation of an uncharacterized Isosphaeraceae member, strain EP7T. Strain EP7T forms round, pink colonies, and spherical, non-motile cells that divide asymmetrically by budding. It grows between 10 and 24 °C and over a range of pH 5 to pH 10. Its genome size is 7.2 Mbp, and its DNA G + C content is 66.7%. Polyphasic characterization justifies the assignment of strain EP7T to a novel species within a novel genus. We introduce the name Kueselia aquadivae for the novel taxon with strain EP7T as the type strain of the novel species. Strain EP7T represents the first Isosphaeraceae member isolated from vadose zone percolate water.
Keywords: Isosphaeraceae; Planctomycetota; Aeration zone; Critical zone; Drainage collectors; Geomicrobiology.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical statement: This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Kolteria novifilia, a novel planctomycetotal strain from the volcanic habitat of Panarea divides by unusual lateral budding.J Bacteriol. 2025 Jul 24;207(7):e0033724. doi: 10.1128/jb.00337-24. Epub 2025 Jun 24. J Bacteriol. 2025. PMID: 40552805 Free PMC article.
-
Marinivivus vitaminiproducens gen. nov., sp. nov., a vitamin B12-producing bacterium isolated from the coral Fungia sp. in South China Sea.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025 Aug;75(8). doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006878. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40824767
-
Vogesella oryzagri sp. nov., isolated from the rhizosphere of rice and in silico genome mining for the prediction of biosynthetic gene clusters.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025 Feb;75(2):006687. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006687. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40009442 Free PMC article.
-
Gaoshiqia hydrogeniformans sp. nov., a novel hydrogen-producing bacterium isolated from a deep diatomaceous shale formation.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025 Jun;75(6). doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006802. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40465470
-
Jejubacter calystegiae gen. nov., sp. nov., moderately halophilic, a new member of the family Enterobacteriaceae, isolated from beach morning glory.J Microbiol. 2020 May;58(5):357-366. doi: 10.1007/s12275-020-9294-1. Epub 2020 Mar 27. J Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32221820
References
-
- Wiegand, S., Jogler, M. & Jogler, C. On the maverick planctomycetes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev.42 (6), 739–760 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M. et al. A global atlas of the dominant bacteria found in soil. Science359 (6373), 320–325 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Bondoso, J. et al. Aquisphaera giovannonii gen. nov., sp. nov., a planctomycete isolated from a freshwater aquarium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. MicroBiol.61 (12), 2844–2850 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Bondoso, J. et al. Community composition of the planctomycetes associated with different macroalgae. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol.88 (3), 445–456 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

