A harbor seal (Phoca vitulina) shows extensive respiratory control in sound production
- PMID: 40890609
- PMCID: PMC12403956
- DOI: 10.1186/s12862-025-02404-9
A harbor seal (Phoca vitulina) shows extensive respiratory control in sound production
Abstract
The duration of animal vocalizations varies between and within species. Which mammals can learn to control this duration? Such respiratory production learning is a scarcely studied subcomponent of vocal learning. Here, we test the hypothesis that harbor seals (Phoca vitulina) are capable of respiratory production learning by testing whether a harbor seal can be trained to i) actively control its vocalization’s duration in two directions (short and long), and ii) exceed the pre-experimental vocalization’s duration (min = 0.202 s, max = 2.621 s). The seal learned to produce uninterrupted vocalizations spanning more than two orders of magnitude in duration, from 79 ms to 9.23 s. Our findings demonstrate a remarkable level of respiratory control in a harbor seal: this respiratory production learning encompasses an extensive range of sound durations and arises at a young age. Producing durations that span such a magnitude is hardly reported in the non-human animal literature; this capacity may be orthogonal to other vocal learning modules and should be tested in more species, both vocal production learners and non-learners.
Supplementary Information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12862-025-02404-9.
Keywords: Animal training; Bioacoustics; Breathing control; Respiratory production learning; Vocal learning.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All training and testing were conducted according to the requirements of the Landesamt für Natur, Umwelt und Verbraucherschutz (LANUV) NRW, Germany, section animal experiment affairs. Upon detailed discussions with the LANUV, the need for approval was waived (file number Az.81–04.78). Informed consent was obtained from all owners of the animals used in the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

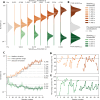
References
-
- Adams A, Vogl W, Dawson C, Raverty S, Haulena M, Skoretz SA. Laryngeal and soft palate valving in the harbour seal (Phoca vitulina). J Exp Biol. 2020;223(20):jeb230201. 10.1242/jeb.230201. - PubMed
-
- Baken RJ. Clinical measurement of speech and voice. London: Taylor & Francis Ltd; 1987.
-
- Blix AS. Adaptations to deep and prolonged diving in phocid seals. J Exp Biol. 2018;221(12):jeb182972. 10.1242/jeb.182972. - PubMed
-
- Boersma P, Weenink D. (2022). Praat: doing phonetics by computer In Glot International (Version 6.2.12) retrieved 17 April 2022 from http://www.praat.org/.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
