Eye Salvage and Vision Preservation in High-Risk Intraocular Retinoblastoma Patients: Long-Term Results From the Prospective Phase II AIEOP RTB 012 Study
- PMID: 40891611
- PMCID: PMC12403015
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.71188
Eye Salvage and Vision Preservation in High-Risk Intraocular Retinoblastoma Patients: Long-Term Results From the Prospective Phase II AIEOP RTB 012 Study
Abstract
Introduction: This study presents the outcomes of high-risk group retinoblastoma (Rb) patients enrolled in the AIEOP RTB 012 Protocol.
Methods: Patients with intraocular unilateral Rb classified as group C/D according to "International Intraocular Retinoblastoma Classification" (IIRC), as well as those with bilateral Rb with at least one eye group C/D/E-IIRC, were treated with four cycles of carboplatin/etoposide combined with focal treatments. The primary endpoint was to evaluate ocular event-free survival (EFS) and overall survival (OS), where events were defined as the need for radiotherapy, eye enucleation, and second-line treatment. Visual acuity (VA) was assessed in all available cases.
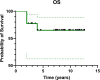
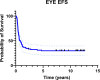
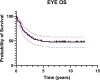
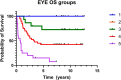
Results: Between February 2012 and September 2017, 60 patients were enrolled (88 eyes), 32 unilateral Rb, 28 bilateral. Twelve eyes were classified as group A/B, 15 group C, 40 group D, and 21 group E. At a median follow-up of 8.71 years, 42/88 eyes were preserved. The 2- and 5-year eye EFS rates were 31.1% (95% CI: 24.4-44.0) and 29.5% (95% CI: 20.4-39.2), respectively. The corresponding 2- and 5-year eye OS rates were 63.3% (95% CI: 52.7-72.7) and 48.9% (95% CI: 38.1-58.8). Ocular survival significantly differed across IIRC groups, with 2- and 5-year survival rates of 100% for group A/B, 86.7% and 73.3% for group C, 65% and 42.5% for group D, and 23.8% and 14.3% for group E, respectively (p < 0.05). No severe toxicity was reported. Among 28 bilateral Rb patients, 12 had VA of at least 20/30 according to the Snellen chart.
Conclusion: The AIEOP RTB 012 protocol has proven to be both safe and effective, ensuring a favorable final VA.
Keywords: high‐risk disease; intraocular; ocular survival; retinoblastoma; visual outcome.
© 2025 The Author(s). Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Second Malignant Neoplasms in Long-term Retinoblastoma Survivors: Retrospective Cohort Study of 491 Patients in Turkey.J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2025 Jul 1;47(5):e161-e167. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0000000000003039. Epub 2025 Apr 21. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40262045
-
Intra-arterial Chemotherapy for Retinoblastoma, Outcomes Analysis in 357 Eyes: Thirteen Years of Experience in a Referral Center in Brazil.Ophthalmol Retina. 2025 Aug;9(8):798-806. doi: 10.1016/j.oret.2025.02.013. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Ophthalmol Retina. 2025. PMID: 39971005
-
Primary Enucleation for Intraocular Unilateral Retinoblastoma Can Save Life in Lower-Income Settings.Semin Ophthalmol. 2025 Aug;40(6):496-500. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2024.2447724. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Semin Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40009000
-
Trilateral retinoblastoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet Oncol. 2014 Sep;15(10):1157-67. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70336-5. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Lancet Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25126964
-
Rapid COJEC versus standard induction therapies for high-risk neuroblastoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 May 19;2015(5):CD010774. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010774.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25989478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fabian I. D., Stacey A. W., Foster A., et al., “Travel Burden and Clinical Presentation of Retinoblastoma: Analysis of 1024 Patients From 43 African Countries and 518 Patients From 40 European Countries,” British Journal of Ophthalmology 105, no. 10 (2021): 1435–1443, 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2020-316613. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Murphree A. L., Villablanca J. G., W. F. Deegan, III , et al., “Chemotherapy Plus Local Treatment in the Management of Intraocular Retinoblastoma,” Archives of Ophthalmology 114 (1996): 1348–1356. - PubMed
-
- Shields C. L., Shields J. A., Needle M., et al., “Combined Chemoreduction and Adjuvant Treatment for Intraocular Retinoblastoma,” Ophthalmology 104 (1997): 2101–2111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

