Diagnostic accuracy of interleukin-6 (IL-6) as a significant biomarker in late-onset neonatal sepsis: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40892314
- PMCID: PMC12405383
- DOI: 10.1007/s00431-025-06409-w
Diagnostic accuracy of interleukin-6 (IL-6) as a significant biomarker in late-onset neonatal sepsis: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
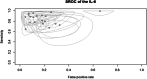
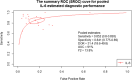
Late-onset neonatal sepsis (LONS) remains a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in neonates, particularly among preterm and low birth weight infants. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) has emerged as a promising biomarker for early detection of LONS, yet the diagnostic performance of IL-6 remains inconsistent across studies. This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the overall diagnostic accuracy of IL-6 in detecting LONS and to assess the certainty of evidence using the GRADE approach. A comprehensive search of five databases was conducted up to July 15, 2025. Twenty-two studies were eligible for inclusion, of which 20 (n = 3527 neonates) were included in the meta-analysis. A bivariate random-effects model was used to estimate pooled sensitivity and specificity, and the area under the SROC curve was used to assess overall diagnostic accuracy. Pooled sensitivity and specificity were 85.2% (95% CI: 80.0-89.3%) and 84.1% (95% CI: 77.5-89.0%), respectively. The positive and negative likelihood ratios were 5.43 and 0.18, with a diagnostic odds ratio of 31.4. The AUC was 0.91, indicating excellent diagnostic accuracy. Subgroup and sensitivity analyses confirmed the robustness of the findings, and no significant threshold effect was detected. However, suspected publication bias was noted. The GRADE assessment rated the certainty of evidence as moderate.
Conclusion: IL-6 demonstrates high diagnostic accuracy for LONS and may serve as a valuable tool for early identification, though standardization of cutoff thresholds and further validation studies are warranted.
What is known: • IL-6 is an early-rising biomarker for late-onset neonatal sepsis (LONS), but its diagnostic accuracy varies across studies.
What is new: • This meta-analysis used a bivariate model to estimate IL-6 performance, yielding high pooled sensitivity (85.2%) and specificity (84.1%).
Keywords: Biomarker; Diagnostic accuracy; IL-6; Interleukin-6; Late-onset neonatal sepsis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval: Not applicable. Consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Singh M, Alsaleem M, Gray CP (2025) Neonatal sepsis. [Updated 2022 Sep 29]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531478/ - PubMed
-
- Lawn JE, Cousens S, Zupan J (2005) 4 million neonatal deaths: when? where? why? Lancet 365(9462):891–900 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources