Gel-Based Ionic Circuits
- PMID: 40892672
- PMCID: PMC12464915
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5c00245
Gel-Based Ionic Circuits
Abstract
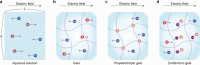
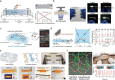
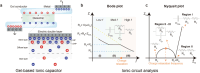
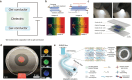
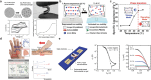
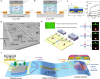
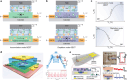
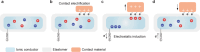
Ionic circuits have emerged as a promising candidate to bridge the gap between biological and artificial systems by applying the mechanically compliant and adaptive nature of gels as ionic conductors. Gel-based ionic circuits exploit the intrinsic characteristics of ions, such as their mass, diversity, and local accumulation, to achieve selectivity, hysteresis, and chemical-electric signal transduction. Their dynamic and nonlinear behaviors not only emulate traditional solid-state electronic systems but also exhibit unique functionalities and operating mechanisms extending beyond established electronic paradigms. In this review, we categorize gel-based ionic circuits into four major functional classes: passive circuit elements, active circuit elements, power sources, and noncircuit elements. We comprehensively discuss the fundamental operating principles, materials strategies, and current challenges, eventually highlighting opportunities for future advancement in ionic devices.
Figures









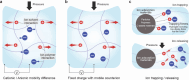
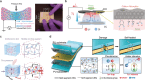
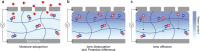







References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

