Phenolic-rich extracts of Teucrium oliverianum confer protection against thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in rats: Insights from metabolomics, biochemical and histopathological analysis
- PMID: 40892759
- PMCID: PMC12404504
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0330595
Phenolic-rich extracts of Teucrium oliverianum confer protection against thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in rats: Insights from metabolomics, biochemical and histopathological analysis
Abstract
Background: Hepatic fibrosis unfolds as a pathological buildup of extracellular matrix triggered by liver injury. Thioacetamide (TAA) plays a versatile role across various fields-from industrial processes and laboratory research to chemical stabilization. Teucrium plants, widely traditional plants, owing to its myriads of pharmacological activities.
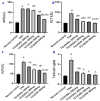
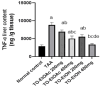
Methods and findings: T. oliverianum ethanolic (TO-EtOH) and ethyl acetate (TO-EtOAc) extracts were explored for their bioactive metabolites via UHPLC-ESI-qTOF-MS/MS that yielded 48 compounds, mainly flavonoids and phenylethanoid glycosides, alongside phenolic acids, iridoid glycosides, and limonoids. Both extracts showed notable hepatoprotective effects in a thioacetamide (TAA)-induced liver injury model, supporting their therapeutic potential. The TAA group showed a significant increase in AST, ALT, ALP, MDA and TNF-α levels concurrent with a significant decrease of GSH level versus normal control group. In contrast, TO-EtOAC and TO-EtOH administered rats showed a decrease in liver enzymes, including ALT, AST, ALP, total bilirubin, and MDA, and an increase in GSH as compared to the TAA model group. Furthermore, both extracts considerably decreased the overall liver TNF-α content inferring anti-inflammatory action. The histo- and immunohistochemical assays of liver tissue of rats in TAA revealed prominent pathological alterations with bridging fibroplasia in multiple hepatic lobules. A restorative effect that improved hepatic morphology with apparent normal hepatic cells and nominal fibroplasia was evident in the administration of both extracts. Among both extracts, TO-EtOH appeared more effective than TO-EtOAC as manifested by a significant improvement in liver's biochemical parameters and structural organization.
Conclusion: This study provides robust evidence supporting the antifibrotic effects of T. oliverianum in a TAA-induced liver injury model. The anti-proliferative activity and hepatoprotective effects are likely to be mediated by its richness in phenolic acids, flavonoids and phenylethanoids.
Copyright: © 2025 Ahmed et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
No Competing Interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Study on the modulation of kidney and liver function of rats with diabetic nephropathy by Huidouba through metabolomics.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:120136. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120136. Epub 2025 Jun 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40513925
-
Caffeoylquinic acids from Silphium perfoliatum L. show hepatoprotective effects on cholestatic mice by regulating enterohepatic circulation of bile acids.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jan 30;337(Pt 2):118870. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118870. Epub 2024 Sep 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39357582
-
Revealing the protective potential of D-(-)-Quinic acid against thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy in rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 26;15(1):31331. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-17356-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40858982 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal management of TAA-induced liver toxicity: Fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2025 Sep;273:156141. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2025.156141. Epub 2025 Jul 23. Pathol Res Pract. 2025. PMID: 40712261 Review.
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
References
-
- Asnaashari S, Dastmalchi S, Javadzadeh Y. Gastroprotective effects of herbal medicines (roots). Int J Food Prop. 2018;21(1):902–20. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2018.1473876 - DOI
-
- Elshamy AI, Abdallah HM, Farrag ARH, Riciputi Y, Pasini F, Taher RF. Artichoke phenolics confer protection against acute kidney injury. Rev Bras Farmacogn. 2020;30:34–42.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

