Bixin from Bixa orellana L.: Analytical Method Validation, Physicochemical Characterization, and Selective Antifungal Activity against Candida spp
- PMID: 40893255
- PMCID: PMC12392009
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c04986
Bixin from Bixa orellana L.: Analytical Method Validation, Physicochemical Characterization, and Selective Antifungal Activity against Candida spp
Abstract
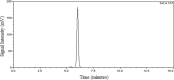
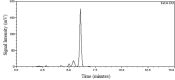
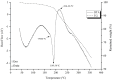
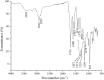
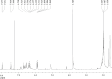
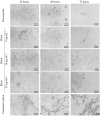
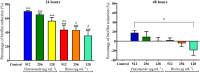
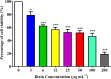
Bixin is a lipophilic apocarotenoid abundant in the aril of Bixa orellana L. seeds. Widely used as a natural colorant in food, textile, and cosmetic industries, its pharmacological potential remains underexplored. This study aimed to extract and purify bixin, characterize its physicochemical properties, develop and validate an HPLC method for quantification, and evaluate its antifungal activity, cytotoxicity, and selectivity in vitro. Extraction was performed by Soxhlet using hexane and chloroform, followed by recrystallization in acetone. Characterization (TG/DTA, FTIR, and 1H NMR) confirmed predominance of the 9'-cis isomer. The HPLC method (λ=470 nm) was validated per ICH Q2-(R2), showing specificity, linearity (R2 = 0.9993), low LOD/LOQ (0.638 and 1.934 μg mL-1), and high precision and accuracy (RSD < 2%; recovery 99.4-100.8%). Antifungal assays against eight Candida strains revealed moderate activity, with MICs from 2 to 256 μg mL-1. The best results were observed for C. glabrata and C. tropicalis (MIC = 2 and 4 μg mL-1). Bixin also inhibited virulence factors inC. albicans Cytotoxicity on Vero cells showed a CC50 of 30.71 μg mL-1, with selectivity indices of 15.36 and 7.68 forC. glabrata andC. tropicalis, respectively. These results support bixin's potential as a natural antifungal agent.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures


References
-
- Atanasov A. G., Waltenberger B., Pferschy-Wenzig E. M., Linder T., Wawrosch C., Uhrin P., Temml V., Wang L. M., Schwaiger S., Heiss E. H., Rollinger J. M., Schuster D., Breuss J. M., Bochkov V., Mihovilovic M. D., Kopp B., Bauer R., Dirsch V. M., Stuppner H.. Discovery and Resupply of Pharmacologically Active Plant-Derived Natural Products: A Review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015;33(8):1582–1614. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.08.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- da Silva V. R. P., Martins N. O., dos Santos C. R., Damas E. B. D., Araujo P. L., Silva G. D., Joanitti G. A., Carneiro M. L. B.. Annatto (Bixa Orellana)-Based Nanostructures for Biomedical Applications-A Systematic Review. Pharmaceutics. 2024;16(10):1275. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101275. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Raddatz-Mota D., Pérez-Flores L. J., Carrari F., Mendoza-Espinoza J. A., de León-Sánchez F. D., Pinzón-López L. L., Godoy-Hernández G., Rivera-Cabrera F.. Achiote (Bixa Orellana L.): A Natural Source of Pigment and Vitamin E. J. Food Sci. Technol.-Mysore. 2017;54(6):1729–1741. doi: 10.1007/s13197-017-2579-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Valarezo E., Torres-Torres S., Pineda-Guarnizo N., Jaramillo-Fierro X., Cartuche L., Morocho V., Meneses M. A.. Study of Essential Oil Isolated from Achiote (Bixa Orellana) Leaves: Chemical Composition, Enantiomeric Distribution and Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Anticholinesterase Activities. Antibiotics. 2023;12(4):710. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12040710. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
