Noninvasive assessment of pulmonary vascular resistance: a synergistic approach using computed tomography pulmonary angiography and echocardiography in pulmonary hypertension
- PMID: 40893543
- PMCID: PMC12397696
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-24-2152
Noninvasive assessment of pulmonary vascular resistance: a synergistic approach using computed tomography pulmonary angiography and echocardiography in pulmonary hypertension
Abstract
Background: Pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) is essential in managing pulmonary hypertension (PH) and has prompted the search for noninvasive assessment techniques. This study investigates the integration of morphological parameters from computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) and functional parameters from transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) to develop a noninvasive method for evaluating PVR in patients with PH.
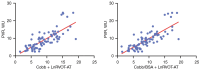
Methods: Data from PH patients who underwent CTPA, TTE, and right heart catheterization (RHC) were analyzed retrospectively. The Cobb angle, defined as the angle between the spine and interventricular septum, was calculated by CTPA. It is assumed that thorax geometry, pericardial morphology, and body surface area (BSA) are factors influencing the Cobb angle measurement, and these factors were adjusted for in the analysis. Multiple linear regression was performed to evaluate the multivariate ability to predict PVR. Multivariate Cox regression analysis assessed the prognostic value of parameters in predicting hospitalization for heart failure.
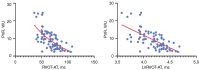
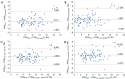
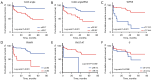
Results: In total, 78 patients meeting the criteria were enrolled. Among the TTE parameters, the right ventricular outflow tract acceleration time (RVOT-AT) demonstrated the best goodness-of-fit to PVR (R2=0.433, P<0.001). Correcting the Cobb angle by BSA significantly improved its fit to PVR (R2=0.510, P<0.001), compared to the uncorrected angle (R2=0.450, P<0.001). The model combining Cobb angle/BSA and RVOT-AT strongly predicted PVR (r=0.815, R2=0.634, P<0.001) and was effective across different demographics. After multivariable adjustment, the Cobb angle [hazard ratio (HR): 1.057; P<0.001], Cobb angle/BSA (HR: 1.087; P<0.001), tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) (HR: 0.878; P=0.014), RVOT-AT (HR: 0.968; P=0.030), and right ventricular myocardial performance index (RVMPI) (HR: 5.324; P<0.001) remained significant independent predictors of heart failure.
Conclusions: The integration of BSA-adjusted morphological markers from CTPA with hemodynamic parameters derived from TTE provides a promising noninvasive method for predicting PVR and demonstrates significant prognostic value in evaluating heart failure in PH patients.
Keywords: Cardiovascular; computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA); pulmonary hypertension (PH); pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR); transthoracic echocardiography (TTE).
Copyright © 2025 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-24-2152/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic Relevance of Tricuspid Annular Plane Systolic Excursion to Systolic Pulmonary Arterial Pressure Ratio and Its Association With Exercise Hemodynamics in Patients With Normal or Mildly Elevated Resting Pulmonary Arterial Pressure.Chest. 2025 Feb;167(2):573-584. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2024.09.013. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Chest. 2025. PMID: 39341493
-
Pulmonary vascular resistance predicts the mortality in patients with bronchiectasis-associated pulmonary hypertension.J Hypertens. 2024 Oct 1;42(10):1703-1710. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003782. Epub 2024 Jun 10. J Hypertens. 2024. PMID: 38860405 Free PMC article.
-
Doppler trans-thoracic echocardiography for detection of pulmonary hypertension in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 9;5(5):CD012809. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012809.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35532166 Free PMC article.
-
Association of hemodynamic and functional variables with pulmonary vasculopathy in lung transplant recipients living at high altitude: A retrospective study.Sci Prog. 2025 Jul-Sep;108(3):368504251367283. doi: 10.1177/00368504251367283. Epub 2025 Aug 17. Sci Prog. 2025. PMID: 40820332 Free PMC article.
-
Echocardiography in newly diagnosed atrial fibrillation patients: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2013 Aug;17(36):1-263, v-vi. doi: 10.3310/hta17360. Health Technol Assess. 2013. PMID: 23985296 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maron BA, Brittain EL, Hess E, Waldo SW, Barón AE, Huang S, Goldstein RH, Assad T, Wertheim BM, Alba GA, Leopold JA, Olschewski H, Galiè N, Simonneau G, Kovacs G, Tedford RJ, Humbert M, Choudhary G. Pulmonary vascular resistance and clinical outcomes in patients with pulmonary hypertension: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Respir Med 2020;8:873-84. 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30317-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoeper MM, Lee SH, Voswinckel R, Palazzini M, Jais X, Marinelli A, Barst RJ, Ghofrani HA, Jing ZC, Opitz C, Seyfarth HJ, Halank M, McLaughlin V, Oudiz RJ, Ewert R, Wilkens H, Kluge S, Bremer HC, Baroke E, Rubin LJ. Complications of right heart catheterization procedures in patients with pulmonary hypertension in experienced centers. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;48:2546-52. 10.1016/j.jacc.2006.07.061 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hull JV, Padkins MR, El Hajj S, Al-Hijji MA, Kanwar A, Crusan DJ, Gulati R, El Sabbagh A, Park JY, Lennon RJ, Behfar A, Rihal CS, Singh M. Risks of Right Heart Catheterization and Right Ventricular Biopsy: A 12-year, Single-Center Experience. Mayo Clin Proc 2023;98:419-31. 10.1016/j.mayocp.2022.07.025 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
