The protein arginine methyltransferase PRMT1 ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing RIPK1-mediated necroptosis and apoptosis
- PMID: 40893679
- PMCID: PMC12399213
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2025.06.005
The protein arginine methyltransferase PRMT1 ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing RIPK1-mediated necroptosis and apoptosis
Abstract
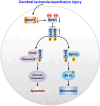
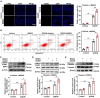
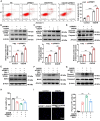
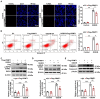
Receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 (RIPK1) plays an essential role in regulating the necroptosis and apoptosis in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. However, the regulation of RIPK1 kinase activity after cerebral I/R injury remains largely unknown. In this study, we found the downregulation of protein arginine methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) was induced by cerebral I/R injury, which negatively correlated with the activation of RIPK1. Mechanistically, we proved that PRMT1 directly interacted with RIPK1 and catalyzed its asymmetric dimethylarginine, which then blocked RIPK1 homodimerization and suppressed its kinase activity. Moreover, pharmacological inhibition or genetic ablation of PRMT1 aggravated I/R injury by promoting RIPK1-mediated necroptosis and apoptosis, while PRMT1 overexpression protected against I/R injury by suppressing RIPK1 activation. Our findings revealed the molecular regulation of RIPK1 activation and demonstrated PRMT1 would be a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Arginine methylation; Cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury; MLKL; Necroptosis; PRMT1; Phosphorylation; RIPK1.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

