WHF Roadmap on Single Pill Combination Therapies
- PMID: 40894085
- PMCID: PMC12396195
- DOI: 10.5334/gh.1457
WHF Roadmap on Single Pill Combination Therapies
Abstract
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading global cause of mortality, with treatment adherence posing a major barrier to effective prevention and control. Single pill combinations (SPCs), also known as fixed-dose combinations, simplify treatment by combining multiple agents into one pill, improving adherence and reducing cardiovascular risk. This World Heart Federation Roadmap synthesizes the latest clinical evidence and identifies key barriers to SPC implementation, including limited manufacturing, affordability, regulatory complexity, and inconsistent guideline inclusion. Drawing on global expert input and health systems analysis, the Roadmap outlines practical, context-specific solutions to improve access, scale-up, and integration of SPCs into national strategies, especially in low- and middle-income countries. It serves as a tool for policymakers, clinicians, and advocates to drive progress in aligning cardiovascular prevention efforts with evidence-based, people-centred care.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; polypill; prevention; single pill combinations.
Copyright: © 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
AD has received speaker honoraria from Astra Zeneca, Sanofi and Bayer and has participated in a research project supported by Bayer. DJP has received honorary speakers from Ferrer, Lepetit, Siemens, and TEVA. Institute of PJ has received funding for polypill related research. MDH has received travel support from the American Heart Association and World Heart Federation. MDH has an appointment at The George Institute for Global Health, which has a patent, license, and has received investment funding with intent to commercialize fixed-dose combination therapy through its social enterprise business, George Medicines. MDH has pending patents for heart failure polypills.
Figures
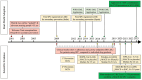
References
-
- Katzmann JL, Sorio-Vilela F, Dornstauder E, Fraas U, Smieszek T, Zappacosta S, et al. Non-statin lipid-lowering therapy over time in very-high-risk patients: effectiveness of fixed-dose statin/ezetimibe compared to separate pill combination on LDL-C. Clin Res Cardiol. 2022;111(3):243–52. DOI: 10.1007/s00392-020-01740-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

