Non-functional oncocytic adrenocortical carcinoma: Case report with clinicopathologic and surgical correlation
- PMID: 40894093
- PMCID: PMC12398781
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eucr.2025.103171
Non-functional oncocytic adrenocortical carcinoma: Case report with clinicopathologic and surgical correlation
Abstract
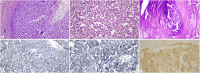
Oncocytic adrenocortical carcinoma (OACC) is a rare variant of adrenocortical carcinoma composed predominantly of oncocytic cells. We present the case of a 45-year-old female with a large, non-functional left adrenal mass diagnosed as OACC. Imaging revealed a well-defined, vascular, heterogeneously enhancing mass without metastasis. Histopathology showed oncocytic cells disposed in nests and sheets with capsular and venous invasion, with low mitotic activity. Surgical excision was curative, and the patient remains disease-free at 10 months. This case highlights the diagnostic and prognostic utility of histologic scoring systems and underlines the role of surgery as the primary treatment in localized OACC.
Keywords: Adrenalectomy; Histopathology; Immunohistochemistry; Incidentaloma; Oncocytic adrenocortical carcinoma; Oncoytic neoplasm.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


References
-
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board . Adrenal Gland Tumours. fifth ed. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2022. Urinary and Male genital tumours.
-
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board . Tumours of the Testis. fifth ed. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2022. Urinary and Male genital tumours.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

