Acylcarnitine enrichment as a characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte metabolic fingerprint
- PMID: 40894250
- PMCID: PMC12398893
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2025.100310
Acylcarnitine enrichment as a characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte metabolic fingerprint
Abstract
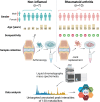
Objective: In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) alter their metabolism to support their activation. We aimed to analyse the full spectrum of metabolic alterations associated with RA by performing untargeted metabolomics in RA FLS vs. non-inflamed (NI) FLS.
Methods: Untargeted annotated metabolomics was performed using mass spectrometry on ten primary RA and seven NI FLS culture extracts and 220 serum samples from participants with early RA from the randomised controlled NORD-STAR trial. Carnitine-related proteins were measured with Western blot. FLS bioenergetic profile was assessed with a Seahorse flux analyser.
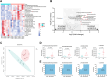
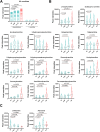
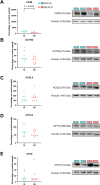
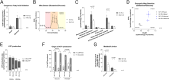
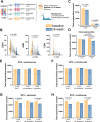
Results: Metabolomics analysis based on 138 annotated metabolites revealed a distinct metabolic fingerprint between RA and NI FLS. Of the 12 metabolites enriched in RA FLS, 11 were acylcarnitines. Pro-inflammatory stimulation of NI FLS also led to acylcarnitine accumulation. RA FLS exhibited lower levels of CD36, a fatty acid transporter, but similar levels of L-carnitine transporter, and carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 A and 2 compared to NI FLS. Seahorse analyses showed no difference in fatty acid oxidation between RA and NI FLS; however, RA FLS displayed mitochondrial dysfunction and energetic impairment. Serum acylcarnitine content decreased after 24 weeks of treatment with methotrexate combined with abatacept or tocilizumab in patients with early RA achieving remission.
Conclusion: Acylcarnitine accumulation is a characteristic of RA FLS metabolic fingerprint and could be linked to mitochondrial dysfunction. In patients with early RA, acylcarnitine content in serum decreases after successful anti-rheumatic treatment. These results indicate a dysregulation in acylcarnitine metabolism in RA at the joint level and systemically.
Keywords: Acylcarnitines; Fibroblast-like synoviocytes; Metabolomics; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:Anna-Karin Ekwall reports a relationship with AbbVie Inc that includes: board membership and consulting or advisory. Anna-Karin Ekwall reports a relationship with Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co KG that includes: speaking and lecture fees. Anna-Karin Ekwall reports a relationship with Pfizer Inc that includes: board membership. Ronald van Vollenhoven reports a relationship with Alfasigma SpA that includes: funding grants. Ronald van Vollenhoven reports a relationship with AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP that includes: consulting or advisory, funding grants, and speaking and lecture fees. Ronald van Vollenhoven reports a relationship with BMS that includes: consulting or advisory, funding grants, and speaking and lecture fees. Ronald van Vollenhoven reports a relationship with Galapagos NV that includes: consulting or advisory, funding grants, and speaking and lecture fees. Ronald van Vollenhoven reports a relationship with MSD France SAS that includes: funding grants. Ronald van Vollenhoven reports a relationship with Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation that includes: funding grants. Ronald van Vollenhoven reports a relationship with Pfizer Inc that includes: consulting or advisory, funding grants, and speaking and lecture fees. Ronald van Vollenhoven reports a relationship with Roche SAS that includes: funding grants. Ronald van Vollenhoven reports a relationship with Sanofi that includes: funding grants. Ronald van Vollenhoven reports a relationship with ucb that includes: consulting or advisory, funding grants, and speaking and lecture fees. Ronald van Vollenhoven reports a relationship with AbbVie Inc that includes: consulting or advisory and speaking and lecture fees. Ronald van Vollenhoven reports a relationship with biogen that includes: consulting or advisory and speaking and lecture fees. Ronald van Vollenhoven reports a relationship with GSK that includes: consulting or advisory and speaking and lecture fees. Ronald van Vollenhoven reports a relationship with Janssen that includes: consulting or advisory and speaking and lecture fees. Ronald van Vollenhoven reports a relationship with remegen that includes: consulting or advisory and speaking and lecture fees. Bjorn Gudbjornsson reports a relationship with Novartis that includes: consulting or advisory and speaking and lecture fees. Bjorn Gudbjornsson reports a relationship with nordic pharma that includes: speaking and lecture fees. Espen A. Haavardsholm reports a relationship with Pfizer that includes: speaking and lecture fees. Espen A. Haavardsholm reports a relationship with ucb that includes: speaking and lecture fees. Espen A. Haavardsholm reports a relationship with abbvie that includes: speaking and lecture fees. Dan Nordstrom reports a relationship with MSD that includes: consulting or advisory and funding grants. Dan Nordstrom reports a relationship with BMS that includes: consulting or advisory. Dan Nordstrom reports a relationship with Lilly that includes: consulting or advisory. Dan Nordstrom reports a relationship with Novartis that includes: consulting or advisory. Dan Nordstrom reports a relationship with Pfizer that includes: consulting or advisory. Dan Nordstrom reports a relationship with ucb that includes: consulting or advisory. Merete Lund Hetland reports a relationship with abbvie that includes: funding grants. Merete Lund Hetland reports a relationship with alfasigma that includes: funding grants. Merete Lund Hetland reports a relationship with BMS that includes: funding grants. Merete Lund Hetland reports a relationship with Eli Lilly that includes: funding grants. Merete Lund Hetland reports a relationship with msd that includes: funding grants. Merete Lund Hetland reports a relationship with Pfizer that includes: funding grants and speaking and lecture fees. Merete Lund Hetland reports a relationship with Sandoz Inc that includes: funding grants and speaking and lecture fees. Merete Lund Hetland reports a relationship with Novartis that includes: funding grants and speaking and lecture fees. Merete Lund Hetland reports a relationship with Nordforsk that includes: funding grants. Merete Lund Hetland reports a relationship with UCB that includes: funding grants and speaking and lecture fees. Merete Lund Hetland reports a relationship with MEDAC that includes: speaking and lecture fees. Mikkel Ostergaard reports a relationship with AbbVie Inc that includes: board membership, consulting or advisory, and funding grants. Mikkel Ostergaard reports a relationship with Amgen Inc that includes: funding grants. Mikkel Ostergaard reports a relationship with BMS that includes: board membership, consulting or advisory, and funding grants. Mikkel Ostergaard reports a relationship with Merck & Co Inc that includes: board membership, consulting or advisory, and funding grants. Mikkel Ostergaard reports a relationship with Celgene SL that includes: board membership, consulting or advisory, and funding grants. Mikkel Ostergaard reports a relationship with Eli Lilly and Company that includes: board membership, consulting or advisory, and funding grants. Mikkel Ostergaard reports a relationship with Novartis that includes: board membership, consulting or advisory, and funding grants. Mikkel Ostergaard reports a relationship with ucb that includes: board membership, funding grants, and speaking and lecture fees. Mikkel Ostergaard reports a relationship with Galapagos that includes: board membership and consulting or advisory. Mikkel Ostergaard reports a relationship with Gilead Sciences Inc that includes: board membership and consulting or advisory. Mikkel Ostergaard reports a relationship with Janssen Pharmaceuticals Inc that includes: board membership and consulting or advisory. Mikkel Ostergaard reports a relationship with MEDAC SAS that includes: consulting or advisory. Till Uhlig reports a relationship with galapagos, Pfizer, UCB that includes: speaking and lecture fees. Sokka-Isler Tuulikki reports a relationship with Amgen, Nordic Medicine that includes: funding grants. Sokka-Isler Tuulikki reports a relationship with AbbVie Inc, Lipum, Pfizer, Nordic Medicine, UCB that includes: speaking and lecture fees. Cristina Maglio reports a relationship with Dagens Medicine that includes: speaking and lecture fees. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

