Ameliorating effect of zinc on water transport in rice plants under saline-sodic stress
- PMID: 40894493
- PMCID: PMC12391086
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1616333
Ameliorating effect of zinc on water transport in rice plants under saline-sodic stress
Abstract
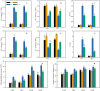
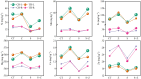
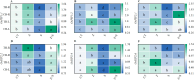
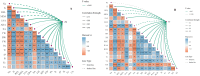
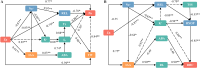
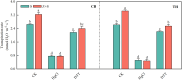
Saline-sodic stress not only impacts the absorption of nutrient ions, such as Zn2+, in rice but also induces physiological water shortages and ion toxicity in rice plants, significantly hindering their growth. To investigate this phenomenon, the present study utilized two rice varieties, 'Changbai 9' and 'Tonghe 899', as test subjects to simulate conditions of saline-sodic soil stress. Four-week-old rice seeds under four treatments: control (CT), 2 μmol L-1 zinc treatment alone (Z), 50 mmol L-1 saline-sodic treatment (S), and 50 mmol L-1 saline-sodic treatment with 2 μmol L-1 zinc (Z+S). The study aimed to examine the effect of zinc on water transport in rice plants under conditions of saline-sodic stress. Research indicates that the application of zinc positively influences the growth of rice under saline-sodic stress.The application of zinc not only reduces the Na+/K+ ratio and malondialdehyde (MDA) content, but also increases the levels of Zn2+, Cu2+, and other ions. Additionally, it enhances the expression of aquaporins in the plasma membrane of rice roots, which in turn increases the hydraulic conductance of the roots and ultimately improves the water absorption capacity of the root system under stress conditions. Additionally, zinc application promotes auxin (IAA) synthesis, facilitating root growth and expanding the root absorption area, which in turn enhances the water absorption rate and helps maintain higher leaf water content. Moreover, zinc application regulates stomatal conductance through an increase in potassium ion concentration and abscisic acid (ABA) content, thereby elevating the transpiration rate of rice leaves and promoting water absorption and transportation within the rice plants. Therefore, the addition of zinc under saline-sodic stress not only alleviates the effects of such stress but also enhances water absorption and transportation in rice plants. This results in a higher water content within the plants, positively influencing their growth and development under saline-sodic conditions.
Keywords: aquaporin; rice; saline-sodic stress; water transport; zinc.
Copyright © 2025 Dang, Tian, Bai, Fu, Cui, Ji, Shao, Geng, Zhang and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Zinc regulation of chlorophyll fluorescence and carbohydrate metabolism in saline-sodic stressed rice seedlings.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 May 27;24(1):464. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05170-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38802756 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated application of organic acids and earthworms improves rhizosphere microbiome, reduces health risks, and modulates proteomic and transcriptomic responses in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under aluminum stress.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2025 Aug 7;303:118817. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2025.118817. Online ahead of print. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2025. PMID: 40779847
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Dressings and topical agents for treating pressure ulcers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 22;6(6):CD011947. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011947.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28639707 Free PMC article.
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
References
-
- Ali M., Niaz Y., Hassan A. G., Ahmad S., Malik Z., Kamran M., et al. (2021). Exogenous zinc induced naCl tolerance in okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) by ameliorating osmotic stress and oxidative metabolism. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 52, 743–755. doi: 10.1080/00103624.2020.1869761 - DOI
-
- Alkharabsheh H. M., Seleiman M. F., Hewedy O. A., Battaglia M. L., Jalal R. S., Alhammad B. A., et al. (2021). Field crop responses and management strategies to mitigate soil salinity in modern agriculture: A review. Agronomy 11. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11112299 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

