This is a preprint.
Deterministic versus Probabilistic Tractography: Impact on White Matter Bundle Shape
- PMID: 40894542
- PMCID: PMC12393354
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.08.19.669949
Deterministic versus Probabilistic Tractography: Impact on White Matter Bundle Shape
Abstract
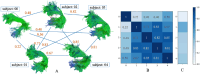
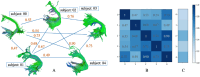
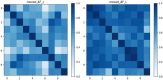
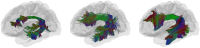
In diffusion MRI-based tractography, deterministic and probabilistic algorithms reconstruct white matter using distinct strategies, yet their impact on bundle morphology remains uncertain. Using bundle shape similarity analysis, we compared both methods for the left arcuate fasciculus (AF_L) (The left arcuate fasciculus is a critical white matter tract that connects language comprehension and production areas in the human brain, enabling fluent language processing) across four datasets: Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI), Human Connectome Project-Aging (HCP-A), National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS), and Pediatric Imaging, Neurocognition, and Genetics (PING). Probabilistic tractography consistently produced higher inter-subject shape similarity, by capturing broader anatomical trajectories and enhancing reproducibility. However, this extensive coverage may obscure subtle pathological variations critical for clinical detection. Bundle shape similarity analysis with atlas corroborated these findings, showing stronger alignment for probabilistic tracking and highlighting its utility in quantitative quality control. These results emphasize the need to balance morphological consistency with sensitivity to neuroanatomical variation when selecting tractography methods for research and clinical applications.
Keywords: Bundle Adjacency; Deterministic Tracking; Diffusion MRI; Probabilistic Tracking; Tractography.
Figures
References
-
- Assaf Y., Johansen-Berg H. & Thiebaut de Schotten M. The role of diffusion mri in neuroscience. NMR in Biomedicine 32 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Mori S., Crain B. J., Chacko V. P. & Van Zijl P. C. Three-dimensional tracking of axonal projections in the brain by magnetic resonance imaging. Annals of Neurology: Official Journal of the American Neurological Association and the Child Neurology Society 45, 265–269 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Parker G. J., Haroon H. A. & Wheeler-Kingshott C. A. A framework for a streamline-based probabilistic index of connectivity (pico) using a structural interpretation of mri diffusion measurements. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 18, 242–254 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Behrens T. E. et al. Characterization and propagation of uncertainty in diffusion-weighted mr imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine: An Official Journal of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 50, 1077–1088 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
