This is a preprint.
MYC and Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Independently Predict Circadian Rhythm Disruption in Lung Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 40894652
- PMCID: PMC12393359
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.08.15.670530
MYC and Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Independently Predict Circadian Rhythm Disruption in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
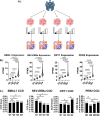
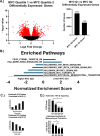
The molecular circadian clock is known to be disrupted in lung adenocarcinoma, and its disruption is pro-tumorigenic in mouse models of this disease. However, the determinants of disruption of the molecular clock in human cancer are not clear. We hypothesized that derangement in expression of specific circadian clock genes or elevated MYC expression could correlate with circadian disruption in human tumors, and used Clock Correlation Distance (CCD) to compare clock order and strength in tumors based on the expression of these genes. While the expression of individual circadian genes did not consistently correlate with disruption, tumors with the highest expression of MYC or high MYC pathway activation had significantly disrupted rhythms compared to those with lower MYC. Unexpectedly, a subset of tumors with very low levels of MYC, below that found in normal lung, also showed disruption of circadian rhythms, prompting us to explore novel determinants of disruption in these tumors. We found that expression of programs associated with epithelial to mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and TGF-β signaling were enriched in tumors with the lowest MYC expression, and that, surprisingly, those tumors with a mesenchymal expression pattern had more ordered (stronger) rhythms. To directly test this correlation between cell state and rhythms, we exposed lung adenocarcinoma cells to TGF- β to induce EMT. TGF- β induced a quasi-mesenchymal phenotype and caused a significant increase in the amplitude of oscillations in these cells. Together, our data show that MYC expression, pathway activation, and a mesenchymal cell state are both independent determinants of circadian status in lung adenocarcinoma.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
A common alteration in effort-based decision-making in apathy, anhedonia, and late circadian rhythm.Elife. 2025 Jun 16;13:RP96803. doi: 10.7554/eLife.96803. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40522113 Free PMC article.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Inhaled mannitol for cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 9;2(2):CD008649. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008649.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 1;5:CD008649. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008649.pub4. PMID: 29424930 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Impact of residual disease as a prognostic factor for survival in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer after primary surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 26;9(9):CD015048. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015048.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36161421 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
