This is a preprint.
Cellular and Molecular Architecture of Renin-Angiotensin System Signaling in the PVN Under Cardiometabolic Stress
- PMID: 40894741
- PMCID: PMC12393292
- DOI: 10.1101/2025.08.14.669892
Cellular and Molecular Architecture of Renin-Angiotensin System Signaling in the PVN Under Cardiometabolic Stress
Abstract
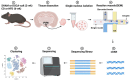
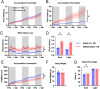
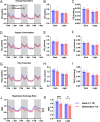
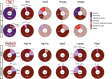
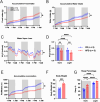
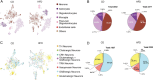
The hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) integrates neuroendocrine and autonomic signals that regulate blood pressure and metabolism. Although the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) is implicated in neurogenic hypertension and obesity, cell-type-specific expression and regulation of its components within the PVN remain poorly understood. Here, we employed single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNA-seq) to profile the transcriptomic landscape of the PVN in male mice under baseline conditions and in models of DOCA-salt-induced hypertension and high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity. We identified major PVN cell types, including neurons, astrocytes, precursor oligodendrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia and endothelial cells, and further resolved eight transcriptionally distinct neuronal subtypes. Expression of RAS-related genes was highly cell-type specific: Agt (angiotensinogen) was enriched in astrocytes, whereas Ace (angiotensin-converting enzyme), Atp6ap2 (also known as the (pro)renin receptor [PRR]), Agtr1a (angiotensin II type 1a receptor, aka AT1aR), Lnpep (leucyl/cystinyl aminopeptidase, aka angiotensin 4 receptor [AT4R]), and the Mas1 proto-oncogene were predominantly expressed in neurons. DOCA-salt treatment increased the proportion of GABAergic and vasopressin neurons and enhanced neuronal Agt and Atp6ap2 expression, while reducing astrocytic Agt, suggesting activation of a vasoconstrictive RAS axis. HFD exposure increased excitatory and stress-responsive neuronal subtypes (glutamatergic, vasopressin, corticotropin-releasing hormone) and upregulated Atp6ap2, Agtr1b, Lnpep, and Mas1 in vasopressin neurons, while downregulating multiple RAS genes in GABAergic neurons. These findings reveal dynamic, cell-type-specific remodeling of RAS signaling in the PVN in response to hypertensive and metabolic stress, providing a transcriptomic atlas of RAS expression in the PVN and identifying potential cellular targets for therapeutic strategies addressing cardiometabolic disorders.
Keywords: DOCA-salt–induced hypertension; high-fat diet–induced obesity; hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus; renin-angiotensin system; single-nucleus RNA sequencing.
Figures







References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
