The role of gut microbiota dysbiosis in drug-induced brain injury: mechanisms and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 40894928
- PMCID: PMC12395749
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1604539
The role of gut microbiota dysbiosis in drug-induced brain injury: mechanisms and therapeutic implications
Abstract
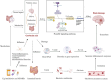
Drug-induced brain injury (DIBI) results from toxicity, interactions or misuse and is increasingly linked to gut-microbiota dysbiosis operating via the gut-brain axis. Disturbed microbial balance drives three core mechanisms-oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and metabolic dysfunction-leading to blood-brain barrier leakage, neuronal loss and cognitive impairment; antibiotics, antineoplastics and psychoactive drugs further promote bacterial translocation and systemic inflammation. Microbial metabolites and neurotransmitters also mediate post-injury anxiety and depression. Restoring microbial equilibrium with probiotics, prebiotics or microbiota transplantation attenuates these pathways and offers a promising therapeutic strategy for DIBI.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; drug-induced brain injury; gut microbiota; gut-brain axis; neuroinflammation.
Copyright © 2025 Zhai, Zhang, Ma, Zhang, Jin, Yan and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dysbiosis and Neurodegeneration in ALS: Unraveling the Gut-Brain Axis.Neuromolecular Med. 2025 Jul 3;27(1):50. doi: 10.1007/s12017-025-08870-0. Neuromolecular Med. 2025. PMID: 40608189 Review.
-
Parkinson's disease and the gut microbiota connection: unveiling dysbiosis and exploring therapeutic horizons.Neuroscience. 2025 Aug 16;581:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2025.07.003. Epub 2025 Jul 2. Neuroscience. 2025. PMID: 40614920 Review.
-
Radiation-induced injury and the gut microbiota: insights from a microbial perspective.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025 Jun 16;18:17562848251347347. doi: 10.1177/17562848251347347. eCollection 2025. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40535532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Gut Microbiota in Modulating Oxidative Stress Induced by Environmental Factors.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2025 Aug 6;59(S2):2-52. doi: 10.33594/000000799. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40851483 Review.
-
Synbiotics, prebiotics and probiotics for solid organ transplant recipients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 20;9(9):CD014804. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014804.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36126902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggrawal A. (2015). Drug-Induced Injury. Accidental and Iatrogenic[J]. 10.1016/B978-0-12-800034-2.00162-2 - DOI
-
- Alzheimer’s disease (2020). Microbiota in neuroinflammation and synaptic dysfunction: a focus on Alzheimer’s disease - PubMed. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35248147/.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

