Distribution of nontuberculous Mycobacteria among presumptive drug resistance tuberculosis patients from a ministry of health drug resistance surveillance program, in western Kenya
- PMID: 40895129
- PMCID: PMC12396555
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jctube.2025.100559
Distribution of nontuberculous Mycobacteria among presumptive drug resistance tuberculosis patients from a ministry of health drug resistance surveillance program, in western Kenya
Abstract
Introduction: Nontuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM) species are emerging pathogens causing Pulmonary diseases with no definitive treatment. Molecular techniques enable characterization and drug resistance profiling, this study sought to determine NTM prevalence, circulating species, and distribution factors among presumptive multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) patients in western Kenya.
Method: Sputum samples were collected between March through October 2022, and transported for testing at Kenya Medical Research Institute (KEMRI) TB laboratory, in Kisumu. The standard NALC-NaOH MGIT culture technique, smear, HAIN AS/CM and NTM drug resistance were carried out.
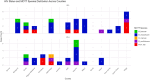
Results: Of the 155 specimens analyzed, 106 (68.4 %) were males, 41 (26.5 %) HIV positive, and participants of ages 36-45 years, the majority. An overall NTM prevalence of 99 (63.9 %), of whom 63 (63 %) among males reported. In addition, 11 NTM species identified, with M. intracellulare (44, 44 %).
Conclusions: High prevalence of NTM species was observed among middle-aged males and HIV negative participants, Kisumu led in distribution (29 %) and among HIV positive. The NTM prevalence among smear negative vs smear positive, was significant a p < 0.001, hence adequate TB/HIV integration and management, use of molecular techniques, and accurate identification is critical.
Keywords: Culture; HIV; Immunocompromised; Macrolides; Multidrug; Nontuberculous; Patients; Presumptive; Prevalence; Pulmonary; Tuberculosis resistance.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- WHO, Global tuberculosis report 2021. Geneva: World Health Organization (in en), 2021.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials