Food hydrocolloids κ-carrageenan and xanthan gum in processed red meat modify gut health in rats
- PMID: 40896518
- PMCID: PMC12392642
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crfs.2025.101162
Food hydrocolloids κ-carrageenan and xanthan gum in processed red meat modify gut health in rats
Abstract
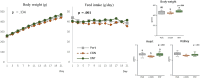
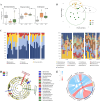
The food hydrocolloids κ-carrageenan and xanthan gum, used in processed foods including meat products, have unclear effects on gut health. This study investigated the effects of incorporating 1 % κ-carrageenan or xanthan gum into pork on protein digestibility, gut microbiota, oxidative stress, and gene expression using both in vitro gastrointestinal digestion/fermentation and an in vivo rodent model. In vitro, xanthan gum reduced protein digestibility (-11 %) in the simulated small intestine, thus elevating protein fermentation metabolites (up to 4-fold), but this was not observed in vivo. Consumption of a low-fiber pork diet without hydrocolloids promoted Akkermansia (29.5 % median abundance) and Tannerellaceae (24.7 %) growth in the colon, whereas κ-carrageenan increased Desulfovibrio (7.95 %) and Alistipes (6.14 %), and xanthan gum enhanced unclassified Muribaculaceae (14.8 %) and Bacteroides (12.1 %). Unexpectedly, transcriptomic analysis revealed a down-regulation of gut inflammatory pathways, accompanied by lower fecal calprotectin levels, in rats consuming pork with hydrocolloids. While κ-carrageenan notably reduced lipid oxidation in stomach contents, only xanthan gum lowered plasma and colonic oxidative stress. These findings highlight the potential of hydrocolloids to modulate dietary responses, suggesting a role in influencing gut health following high processed meat consumption.
Keywords: Akkermansia; Food additives; Gut microbiota; Pork; Protein digestibility.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this manuscript.
Figures
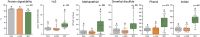


Similar articles
-
Impact of pectin or xanthan addition to mashed potatoes gelled with κ-carrageenan on texture and rheology, oral processing behavior, bolus properties and in mouth starch digestibility.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 May;308(Pt 1):142349. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.142349. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40120903
-
The Impact of Ink Composition and Its Physical Properties on the Selected Attributes of 3D-Printed Fruit Purées with Hydrocolloid Molecules.Molecules. 2025 Aug 15;30(16):3394. doi: 10.3390/molecules30163394. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40871547 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of extruded corn distillers dried grains with solubles on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, gut health, and microbiota diversity in weaned piglets.J Anim Sci. 2025 Jan 4;103:skaf120. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaf120. J Anim Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244394
-
Application of various hydrocolloids in fruit-based beverages to improve their properties: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Jul;318(Pt 4):145251. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.145251. Epub 2025 Jun 13. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40517869 Review.
-
The role of fiber in modulating plant protein-induced metabolic responses.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025;65(23):4599-4614. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2024.2392149. Epub 2024 Aug 17. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39154210 Review.
References
-
- Cao C., Yuan D., Kong B., Chen Q., He J., Liu Q. Effect of different κ-carrageenan incorporation forms on the gel properties and in vitro digestibility of frankfurters. Food Hydrocoll. 2022;129 doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107637. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

