Flavour formation in the coffee substitute 'lupin coffee' related to the formation of acrylamide
- PMID: 40896652
- PMCID: PMC12397916
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102919
Flavour formation in the coffee substitute 'lupin coffee' related to the formation of acrylamide
Abstract
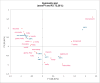
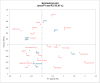
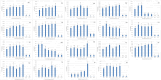
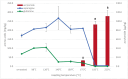
A coffee substitute derived from sweet lupins (Lupinus angustifolius L.) was investigated for the first time with regard to the impact of the roasting process on flavour formation, acrylamide generation, and amino acid behaviour. Roasting was carried out batchwise at temperatures between 98 °C to 220 °C. 55 volatile compounds were semi-quantified using headspace SPME GC-MS. Maillard reaction products, particularly substituted pyrazines and furans, constituted the majority of the volatiles formed. The flavour of "lupin coffee" was described as strongly roasted and reminiscent of coffee, though less complex than traditional coffee. Flavour development became evident at temperatures of 195 °C and above. The highest acrylamide concentration detected was 111 μg/kg at 220 °C which is considerably below the EU benchmark levels established for coffee substitutes. This work provides a solid foundation for future investigations aimed at minimising process contaminants while preserving the desired flavour.
Keywords: Acrylamide; Amino acids; Coffee substitute; Flavour formation; Lupin seeds (Lupinus angustifolius L.); Roasting.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Generation of Maillard reaction-derived flavour compounds in coffee analogues by an extrusion-based solid model system.Food Chem. 2025 Nov 15;492(Pt 3):145552. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2025.145552. Epub 2025 Jul 14. Food Chem. 2025. PMID: 40680419
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Unveiling the Impact of Infrared Drying on the Quality of Coffee Leaves: A Comprehensive Analysis of Physicochemical Indices, Antioxidant Potential, Maillard Reaction Products, and Aroma Profile.J Food Sci. 2025 Jul;90(7):e70400. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.70400. J Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 40660489
-
The quantity, quality and findings of network meta-analyses evaluating the effectiveness of GLP-1 RAs for weight loss: a scoping review.Health Technol Assess. 2025 Jun 25:1-73. doi: 10.3310/SKHT8119. Online ahead of print. Health Technol Assess. 2025. PMID: 40580049 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdel-Haleem A.M.H., Abdel-Aty M.M. The relationship between varieties and acrylamide formation in roasted barley. Egyptian Journal of Chemistry. 2021;64(9):5357–5372. doi: 10.21608/ejchem.2021.82852.4080. - DOI
-
- Adi P., Mulyani R., Yudhistira B., Punthi F., Listyaningrum R.S., Chang C.K.…Hsieh C.W. Improving flavor, safety, and sustainability of coffee substitute: Challenges and future research directions. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2025;162 doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2025.105083. - DOI
-
- Anese M. In: Acrylamide in food. Gökmen V., Mogol B.A., editors. Academic Press; London, UK: 2023. Acrylamide in coffee and coffee substitutes; pp. 185–200. ISBN 978-0-323-9919-3. https://10.1016/B978-0-323-99119-3.00020-5.
-
- Becalski A., Halldorson T., Hayward S., Roscoe V. Furan, 2-methylfuran and 3-methylfuran in coffee on the Canadian market. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis. 2016;47:113–119. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2016.01.006. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

