A20 inhibits doxorubicin-induced macrophage maturation and apoptosis through mTOR signaling in classical Hodgkin lymphoma
- PMID: 40896706
- PMCID: PMC12399062
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2025.86862.18767
A20 inhibits doxorubicin-induced macrophage maturation and apoptosis through mTOR signaling in classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Abstract
Objectives: Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) is identified by the appearance of Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. A20 and CYLD are deubiquitinating enzymes involved in negatively regulating NF-κB-mediated immune response. Vincristine (Vinc) and doxorubicin (Dox) are classical antitumor drugs, in which Dox serves a key role in chemotherapy against cHL and Vinc induces disruption of microtubule function that inhibits mitosis of cancer cells. Little is known about the roles of A20/CYLD in regulating macrophage function from cHL patients upon treatment with Vinc or Dox. This study, therefore, asked whether A20/CYLD expression affects function of macrophages in cHL cases.
Materials and methods: Macrophages from cHL patients differentiated from bone marrow cells were exposed to Vinc or Dox. Gene expression levels were determined by real time-qPCR, cell maturation, apoptosis and phagocytosis by flow cytometry, and cytokine release by ELISA.
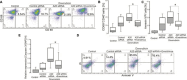
Results: Dox induced maturation, apoptosis, and phagocytosis of macrophages in cHL cases. Moreover, the percentage of CD68+CD40+, but not CD68+CD86+ cells as well as levels of IL-1β were further enhanced when exposed to A20 siRNA, whereas the absence of CYLD unaltered macrophage function in cHL patients. Importantly, the increased numbers of A20-sensitive CD68+CD40+ and Annexin V-PI+ cells as well as enhanced levels of caspase 3 were abolished in the presence of mTOR inhibitor Everolimus.
Conclusion: The present study indicates that Dox-induced macrophage maturation and apoptosis are dependent on A20 expression through mTOR signaling. Moreover, inhibition of Dox-induced macrophage maturation in the patients with low A20 expression by Everolimus might represent a promising therapy for A20-sensitive cHL cases.
Keywords: A20; Classical hodgkin lymphoma; Everolimus; IL-1β; Macrophages.
© 2025. This work is openly licensed via CC BY 4.0.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this paper declare that they have no financial/commercial conflicts of interests.
Figures



References
-
- Mathas S, Hartmann S, Kuppers R. Hodgkin lymphoma: Pathology and biology. Semin Hematol. 2016;53:139–147. - PubMed
-
- Janku F, Park H, Call SG, Madwani K, Oki Y, Subbiah V, et al. Safety and efficacy of vorinostat plus sirolimus or everolimus in patients with relapsed refractory hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26:5579–5587. - PubMed
-
- Cencini E, Fabbri A, Rigacci L, Lazzi S, Gini G, Cox MC, et al. Evaluation of the prognostic role of tumour-associated macrophages in newly diagnosed classical Hodgkin lymphoma and correlation with early FDG-PET assessment. Hematol Oncol. 2017;35:69–78. - PubMed
-
- Panico L, Tenneriello V, Ronconi F, Lepore M, Cantore N, Dell‘Angelo AC, et al. High CD20+ background cells predict a favorable outcome in classical Hodgkin lymphoma and antagonize CD68+ macrophages. Leuk Lymphoma. 2015;56:1636–1642. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Huang R, Liu L, Meng Y, Liu X. Epigenetic abnormalities of classical Hodgkin lymphoma and its effect on immune escape. Cell Biochem Funct. 2020;38:242–248. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
