Early-onset colorectal cancer patients exhibit a distinct molecular fingerprint: insights from a large-scale NGS study of 1209 patients
- PMID: 40896878
- PMCID: PMC12424413
- DOI: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2025.105756
Early-onset colorectal cancer patients exhibit a distinct molecular fingerprint: insights from a large-scale NGS study of 1209 patients
Abstract
Background: Early-onset colorectal cancer (EO-CRC, ≤50 years of age) exhibits unique clinical and biological characteristics when compared with average-onset CRC (AO-CRC), but its overall molecular profile is still not well studied.
Materials and methods: We retrospectively analysed 1209 patients with metastatic CRC profiled using FoundationOne® CDx, a clinically validated next-generation sequencing assay targeting 324 cancer-related genes. Patients were classified as EO-CRC (n = 298) or AO-CRC (n = 911). Genomic alterations, including amplifications, deletions, and point mutations, were compared between the groups. Overall survival (OS) was assessed through 1 : 1 propensity-score-matched cohorts adjusted for key clinical and molecular covariates.
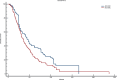
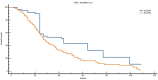
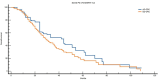
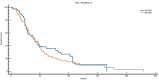
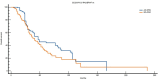
Results: Patients with EO-CRC showed a unique genomic profile marked by a higher incidence of MYC, RAD21, GNAS, and MAPK1 amplifications. They also experienced CDKN2B loss and recurrent mutations, including APC∗, NRAS Q61L, PIK3CA, and TP53 G266V. These variations were statistically significant, indicating different oncogenic pathways. When comparing matched analyses, patients with EO-CRC had notably poorer OS than those with AO-CRC: 35 months versus 41 months in the overall matched group (P = 0.0326), 35 months compared with 44 months among Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status 0 patients (P = 0.0026), and 27 months versus 44 months in the RAS/BRAF-mutated subgroup (P = 0.0024).
Conclusions: Patients with EO-CRC show a distinctive and biologically aggressive molecular profile, marked by significant changes in genes associated with cell proliferation and responses to environmental stress. These observations support the classification of EO-CRC as a potentially distinct clinical entity and suggest that personalised treatment strategies tailored to age-related molecular profiles warrant further investigation.
Keywords: early-onset colorectal cancer; metastatic colorectal cancer; molecular profiling; next-generation sequencing; precision oncology.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Wagle N.S., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(1):17–48. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

