Displacement-encoded MRI reveals biomechanical stiffening in rheumatoid arthritis wrists: a case control study
- PMID: 40897783
- PMCID: PMC12405489
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-17316-3
Displacement-encoded MRI reveals biomechanical stiffening in rheumatoid arthritis wrists: a case control study
Abstract
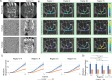
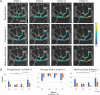
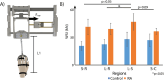
Identifying and diagnosing early-stage rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has remained an unmet challenge in medicine and a roadblock to identifying treatments at time points when disease-modifying therapies may be most effective. Recent studies have demonstrated that imaging the response of cartilage under mechanical loading, as well as alterations in matrix macro- and micro-molecule composition, could serve as potential biomarkers to identify tissue degeneration. Therefore, the objective of this paper was to identify RA-related cartilage degeneration in human wrists using novel MRI techniques. We applied in vivo displacement-encoded MRI to human wrists during cyclic radioulnar deviation, along with the quantitative MRI methods (T1ρ, T2, T2*) during a static condition, to a small healthy and RA patient cohort (6 healthy, 4 RA). We then used a linear mixed-effects model to identify key factors affecting the results. We found that the RA patients had wrists with higher torsional stiffness by approximately 2-fold compared to the control group. The RA group showed lower intercarpal joint displacements by roughly half of the control group, and some joint regions indicated tissue softening. We also found that the quantitative MRI metrics showed non-significant differences between control and RA groups (the T2 and T2* of the RA group was roughly 10% and 5% more than the control group, respectively), however, differences were detected among regions in T2 and T2* metrics. This study demonstrated that displacement-encoded MRI may be a promising method to distinguish functional and noninvasive metrics between RA and healthy wrists, and may provide a means to distinguish the disease state compared to conventional imaging methods.
Keywords: Cartilage; Cartilage degeneration; Wrist; dualMRI; qMRI.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at the University of Colorado, Anschutz.
Figures


References
-
- Ilan, D. I. & Rettig, M. E. Rheumatoid arthritis of the wrist. Bull. NYU Hosp. Jt. Dis.61, 179 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Trieb, K. Treatment of the wrist in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Hand Surg. Am.33, 113–123 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Genant, H. K. et al. Assessment of rheumatoid arthritis using a modified scoring method on digitized and original radiographs. Arthritis Rheum.41, 1583–1590 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Leak, R. S., Rayan, G. M. & Arthur, R. E. Longitudinal radiographic analysis of rheumatoid arthritis in the hand and wrist. J. Hand Surg. Am.28, 427–434 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Rainbow, M. J., Wolff, A. L., Crisco, J. J. & Wolfe, S. W. Functional kinematics of the wrist. J. Hand Surg. Eur. Vol. 41, 7–21 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

