Genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies Menin and SUZ12 as regulators of human developmental timing
- PMID: 40897805
- PMCID: PMC12431854
- DOI: 10.1038/s41556-025-01751-5
Genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies Menin and SUZ12 as regulators of human developmental timing
Abstract
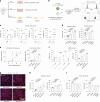
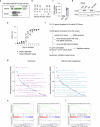
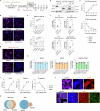
Embryonic development follows a conserved sequence of events across species, yet the pace of development is highly variable and particularly slow in humans. Species-specific developmental timing is largely recapitulated in stem cell models, suggesting a cell-intrinsic clock. Here we use directed differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into neuroectoderm to perform a whole-genome CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screen and show that the epigenetic factors Menin and SUZ12 modulate the speed of PAX6 expression during neural differentiation. Genetic and pharmacological loss-of-function of Menin or SUZ12 accelerate cell fate acquisition by shifting the balance of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 at bivalent promoters, thereby priming key developmental genes for faster activation upon differentiation. We further reveal a synergistic interaction of Menin and SUZ12 in modulating differentiation speed. The acceleration effects were observed in definitive endoderm, cardiomyocyte and neuronal differentiation paradigms, pointing to chromatin bivalency as a general driver of timing across germ layers and developmental stages.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: L.S. is a scientific cofounder and paid consultant of BlueRock Therapeutics Inc. and a cofounder of DaCapo Brainscience. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures












References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UM1 HG012654/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS128087/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- R01 NS128087/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1HG012654/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

