Impact upfront: novel format for Novo Nordisk Foundation funding
- PMID: 40898205
- PMCID: PMC12403301
- DOI: 10.1186/s12961-025-01385-x
Impact upfront: novel format for Novo Nordisk Foundation funding
Abstract
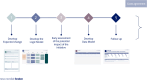
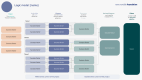
Many retrospective assessments of the wider, societal impacts from health research funding use the Payback Framework or other frameworks. Much of this experience was collated in the 2018 Statement by the International School on Research Impact Assessment (ISRIA). Despite increased interest, especially in engaged research and a wider range of evaluation approaches, rarely do health and other research funders take a prospective approach and analyse the potential impact from a proposal to inform an impact management approach aimed at boosting impact. In this paper, experts from the Novo Nordisk Foundation, a leading philanthropic funder of research, describe how they are developing and applying such a pioneering approach. The five steps form a continuum from project inception to data collation and assessment. The first step entails preparing the project's narrative in alignment with the project's vision. The second, building the logic model, includes defining success factors and effect chains. The third is an early assessment of the initiative's potential impact, conducted on a case basis. The fourth is implementing the data model by integrating specific indicators. The fifth focuses on monitoring, impact management and creating impact products, including developing a comprehensive plan for data reporting and assessment, with scope for adjustments based on experience. This approach aligns with ISRIA guidelines, but further steps are needed. Whilst the Foundation is driving innovation in impact assessment by successfully introducing a new approach that uses prospective impact analysis to inform impact management to enhance the levels of impact achieved, further progress is needed on stakeholder engagement expanding towards a more inclusive stakeholder involvement.
Keywords: Impact framework; Impact management; Intervention logic; Novo Nordisk Foundation; Payback Framework; Prospective assessment; Research funders; Research impact; Societal benefits; Theory-of-change.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. This opinion paper relies on publicly available publications and the experience of the authors. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: G.V.B., H.B.F. and K.Z.I. are employees of NNF. S.H. received an honorarium from NNF for reviewing a draft report on the impact from NNF-funded research.
Figures




References
-
- Buxton M, Hanney S. How can payback from health services research be assessed?’. J Health Serv Res Policy. 1996;1:35–43. 10.1177/1355819696001001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

