Validated methods for isolation and qualification of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells from different sources
- PMID: 40898279
- PMCID: PMC12403454
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-025-06972-8
Validated methods for isolation and qualification of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells from different sources
Abstract
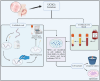
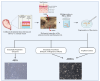
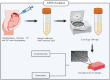
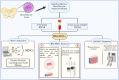
Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells (MSCs) have attracted considerable attention in the field of regenerative medicine. Their unique properties make them suitable for various therapeutic applications. This article reviews accepted methods and guidelines for the isolation and characterization of MSCs from various sources. Common sources include bone marrow, adipose tissue, perinatal and umbilical cord tissue, dental pulp, etc. Naturally, the techniques used to isolate MSCs can vary depending on the source from which they are derived. However, several methods have been widely accepted by the scientific community. These include enzymatic digestion, density gradient centrifugation, the use of Percoll, adherence-based techniques and selective culture conditions. To characterize MSCs, basic criteria established by the International Society for Cell and Tissue Transplantation and the International Federation for Adipose Tissue are routinely used. These criteria include the ability of MSCs to adhere to plastic surfaces under standard culture conditions, the expression of specific membrane markers and their differentiation potential. Various techniques are used to assess these characteristics, including mixed lymphocyte reactions, flow cytometry and immunophenotyping profiles. These assessments aim to confirm the purity of the MSCs and validate their mesenchymal properties. In summary, the isolation and characterization of MSCs requires careful consideration of the different available methods. Each source presents unique challenges and advantages. By following established guidelines, researchers can ensure successful isolation and characterization of MSCs. This knowledge will ultimately improve their use in regenerative medicine.
Keywords: Characterization of MSCs; Isolation of MSCs; Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells (MSCs).
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
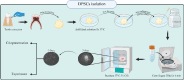

References
-
- Jansen J. The first successful allogeneic bone-marrow transplant: Georges Mathe. Transfus Med Rev. 2005;19(3):246–8. - PubMed
-
- Caplan AI. Mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 1991;9(5):641–50. - PubMed
-
- Friedenstein AJ, Petrakova KV, Kurolesova AI, Frolova GP. Heterotopic of bone marrow. Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues. Transplantation. 1968;6(2):230–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

