Investigating the mechanism of artemisinin in treating osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics, network pharmacology, and molecular docking
- PMID: 40898503
- PMCID: PMC12401449
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000042281
Investigating the mechanism of artemisinin in treating osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics, network pharmacology, and molecular docking
Abstract
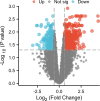
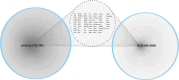
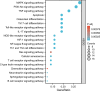
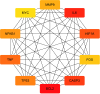
This study aims to explore the mechanism of artemisinin in treating osteoarthritis (OA) through bioinformatics and network pharmacology. The targets of artemisinin were obtained from databases such as TCMSP, and the disease targets of OA were screened from OMIM, TTD, DisGeNET, and GEO databases. The predicted targets of artemisinin were intersected with OA disease targets to obtain drug-disease common targets, which were visualized using a Venn diagram. Gene ontology (GO) analysis and KEGG functional analysis was performed on the 68 common target genes, and protein interaction network analysis was conducted to analyze their interaction relationships. The key genes were identified using the Cytohubba algorithm, followed by molecular docking with AutoDockTools 1.5.7 software and PyMOL software. Through database screening, 464 targets of artemisinin were identified, and 1654 OA target genes were screened from databases and GEO chip databases. The intersection of drug targets and disease targets yielded 68 drug-disease common targets. GO and KEGG analysis showed that these common target genes are mainly involved in oxidative stress response, bone formation, response to bacterial molecules, response to lipopolysaccharide, response to hypoxia, response to xenobiotic stimuli. Their molecular functions include regulation of transcription factor binding, ubiquitin-protein ligase activity, cytokine receptor binding. These common targets are enriched in 36 signaling pathways, including MAPK signaling pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, TNF signaling pathway, IL-17 signaling pathway, NF-Kappa B signaling pathway, which are key regulatory pathways in the development of OA. Through protein interaction analysis and Cytohubba algorithm, 10 key genes were obtained. Furthermore, the top 5 key genes (BCL-2, IL-6, CASP3, HIF1A, TNF) were molecular-docked with artemisinin, and the results showed that these molecules could form stable binding through hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interaction. Artemisinin may exert drug efficacy through multi-target and multi-pathway synergism in the treatment of OA. This study provides an effective theoretical basis for the treatment of OA with artemisinin.
Keywords: artemisinin; bioinformatics; molecular docking; network pharmacology; osteoarthritis.
Copyright © 2025 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Zhong G, Liang R, Yao J, et al. Artemisinin ameliorates osteoarthritis by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51:2575–90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

