Integrative Analysis of Key Signalling Pathways in Neural Tube Defects: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies
- PMID: 40898587
- PMCID: PMC12405674
- DOI: 10.1002/jdn.70051
Integrative Analysis of Key Signalling Pathways in Neural Tube Defects: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
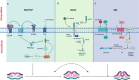
Neural tube defects (NTDs), such as anencephaly and spina bifida, are prevalent congenital anomalies of the central nervous system. These defects can give rise to severe lifelong disabilities and incur substantial healthcare expenses for the affected individuals. The occurrence of NTDs is caused by multiple factors, including molecular regulatory mechanisms and environmental factors. This article comprehensively reviews the underlying mechanisms of three crucial signalling pathways associated with neural tube development: the Wnt/Planar Cell Polarity (PCP) signalling pathway, the Sonic Hedgehog signalling pathway and the Notch signalling pathway, and, on this basis, delves into the potential molecular therapeutic strategies for NTDs. This review is of great significance for comprehensively elucidating the molecular causes of NTDs and expanding prevention and treatment strategies for related congenital anomalies.
Keywords: NTDS; Notch signalling pathway; Sonic Hedgehog signalling pathway; Wnt/PCP signalling pathway; anencephaly; spina bifida.
© 2025 The Author(s). International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Society for Developmental Neuroscience.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Allache, R. , Wang M., de Marco P., Merello E., Capra V., and Kibar Z.. 2015. “Genetic Studies of ANKRD6 as a Molecular Switch Between Wnt Signaling Pathways in Human Neural Tube Defects.” Birth Defects Research. Part A, Clinical and Molecular Teratology 103, no. 1: 20–26. 10.1002/bdra.23273. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

