Anti-Parkinsonian 4-hydroxy-2-pyridones from an endolichenic fungus, Tolypocladium sp. (strain CNC14)
- PMID: 40899779
- PMCID: PMC12455187
- DOI: 10.1093/jimb/kuaf027
Anti-Parkinsonian 4-hydroxy-2-pyridones from an endolichenic fungus, Tolypocladium sp. (strain CNC14)
Abstract
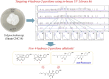
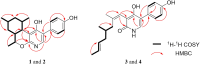
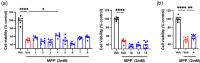
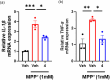
4-Hydroxy-2-pyridone alkaloids have attracted considerable attention because of their intriguing structures and diverse bioactivities. In our previous study, 4-hydroxy-2-pyridone alkaloids were shown to exhibit potent activity against neuron-associated targets. To discover this class of neuroactive compounds, an array of endolichenic fungal extracts was screened by analyzing liquid chromatography-ultraviolet-mass spectrometry (LC-UV-MS) profiles. The screening yielded strain Tolypocladium sp. (strain CNC14), which produced compounds with characteristic Ultraviolet patterns for 4-hydroxy-2-pyridone alkaloids using our in-house library. Based on these findings, we conducted a chemical investigation, which led to the isolation of four new (1-4) and ten known (5-14) compounds. Their structures were elucidated via spectroscopic methods such as nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry. The stereochemistry of the new compounds (1-4) was established using rotating frame overhauser effect spectroscopy (ROESY), and the electronic circular dichrosim (ECD) was compared with the calculated data. Interestingly, the side chains of 4-hydroxy-2-pyridone in 1 and 2 were cyclized in different directions to form benzopyrano[3,4-b]pyridinol from previously reported compounds, and all the new compounds were predicted to be biosynthesized from reduced tolypyridone C (7) via the hetero-Diels-Alder reaction. Among the isolated compounds, 4 significantly protected neuronal cells against treatment with 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+), a Parkinsonian neurotoxin, in an in vitro Parkinson's disease model. One-Sentence Summary: Four new neuroprotective 4-hydroxy-2-pyridone alkaloids were discovered from an endolichenic fungus Tolypocladium sp.
Keywords: Tolypocladium sp; 4-Hydroxy-2-pyridone alkaloids; Endolichenic fungus; Parkinson's disease.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Society of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
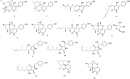



References
-
- Bae J. E., Kim J. B., Jo D. S., Park N. Y., Kim H. Y., Lee J. H., Kim S. H., Kim S. H., Son M., Kim P., Ryu H. Y., Lee W. H., Ryoo Z. Y., Lee H. S., Jung Y. K., Cho D. H. (2022). Carnitine protects against MPP+-induced neurotoxicity and inflammation by promoting primary ciliogenesis in SH-SY5Y. Cells, 11(17), 2722. 10.3390/cells11172722 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bang S., Song J. H., Lee D., Lee C., Kim S., Kang K. S., Lee J. H., Shim S. H. (2019). Neuroprotective secondary metabolite produced by an endophytic fungus, Neosartorya fischeri JS0553, isolated from Glehnia littoralis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 67(7), 1831–1838. 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b05481 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Choi H. K., Shim S. H. (2017). Tricyclic pyridone alkaloids from cultures of cornus officinalis fruits-associated fungus, fusarium lateritium SSF2. Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy, 48, 268–272.
-
- Eo H., Kwon Y., Huh E., Sim Y., Choi J. G., Jeong J. S., Du X. F., Soh H. Y., Hong S. P., Kim P. Y., Oh M. S. (2019). Protective effects of DA-9805 on dopaminergic neurons against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity in the models of Parkinson's. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherpy, 117, 109184. 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109184 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

