Eradication of Extensive Lymph-Node, Bone and Pleural Metastases of a Breast-Cancer Patient Treated With Radiation, Immunotherapy and Oral Recombinant Methioninase
- PMID: 40900890
- PMCID: PMC12401033
- DOI: 10.21873/cdp.10476
Eradication of Extensive Lymph-Node, Bone and Pleural Metastases of a Breast-Cancer Patient Treated With Radiation, Immunotherapy and Oral Recombinant Methioninase
Abstract
Background/aim: Metastatic breast cancer is a recalcitrant disease with a poor prognosis. Novel targets and therapies are necessary to improve the survival rate of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Previous pre-clinical and clinical studies, have demonstrated the effectiveness of oral recombinant methioninase (o-rMETase) against breast cancer. The present case report shows that combination treatment with radiation, immunotherapy, a low-methionine diet, and o-rMETase led to rapid eradication of extensive bone and other metastases in a patient with breast cancer.
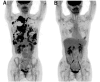
Case report: A patient with breast cancer with extensive metastases to the liver, lymph nodes, pleura and bones was diagnosed using [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET). The patient was immediately started on systemic drug therapy with tamoxifen and leuprorelin, but it failed to suppress the tumor. Then, combination treatment with radiation, immunotherapy with biological response modifier (BRM)-activated killer (BAK), a low-methionine diet, and o-rMETase was started as second-line treatment. Five months after beginning of the combination treatment, the patient had a subsequent FDG-PET scan and extensive eradication of almost all metastases was observed, with only a metastasis remaining in the liver.
Conclusion: o-rMETase in combination with immunotherapy and irradiation eradicated extensive metastases in a patient with breast cancer. Further investigation of this combination treatment for breast cancer is necessary including clinical trials.
Keywords: BAK; Breast cancer; FDG-PET; Hoffman effect; eradication; immunotherapy; metastasis; methionine addiction; oral recombinant methioninase; radiation.
©2025 The Author(s). Published by the International Institute of Anticancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no competing interests regarding this work.
Figures
References
-
- Kubota Y, Han Q, Masaki N, Hozumi C, Hamada K, Aoki Y, Obara K, Tsunoda T, Hoffman RM. Elimination of axillary-lymph-node metastases in a patient with invasive lobular breast cancer treated by first-line neo-adjuvant chemotherapy combined with methionine restriction. Anticancer Res. 2022;42(12):5819–5823. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.16089. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
