Subcutaneous Panniculitis-Like T-Cell Lymphoma in Children: Two Case Reports
- PMID: 40900900
- PMCID: PMC12399884
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S538418
Subcutaneous Panniculitis-Like T-Cell Lymphoma in Children: Two Case Reports
Abstract
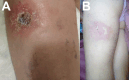
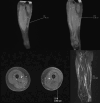
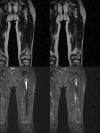
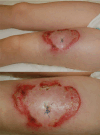
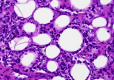
Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma (SPTCL) is a rare primary cutaneous lymphoma derived from cytotoxic αβ T cells, clinically and histopathologically resembling inflammatory diseases of adipose tissue, particularly lupus panniculitis. It accounts for <1% of all non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, with approximately 20% of cases occurring in children. The main aim of this paper was to present two pediatric cases of SPTCL, highlighting the diagnostic challenges involved. The first patient, a 5-year-9-month-old boy, was admitted with a 15 cm infiltrative lesion on the left thigh, previously misdiagnosed and unsuccessfully treated with antibiotics. Imaging revealed an infiltrate resembling lymphedema. A biopsy confirmed SPTCL with a typical immunophenotype. The patient received EURO-LB 02 protocol therapy for peripheral T-cell lymphoma, complicated by pancytopenia, respiratory infection, and polyneuropathy. Post-treatment follow-up showed lesion regression, with residual subcutaneous atrophy (5 cm). The second patient, a 7-year-old girl, presented with a 10 cm inflammatory lesion on the left thigh and systemic symptoms. Imaging and histopathology confirmed the diagnosis. She was treated with the same protocol. Three years later, disease recurrence occurred on the left forearm, managed with alemtuzumab and methotrexate. Both patients remain under outpatient follow-up. Despite its rarity, SPTCL poses a significant diagnostic challenge in children. Accurate differentiation and early diagnosis are crucial for prompt and effective treatment.
Keywords: children; differential diagnosis; pediatric; skin diseases; subcutaneous panniculitis-like T-cell lymphoma.
© 2025 Mitura-Lesiuk et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Subcutaneous Panniculitis-Like T-Cell Lymphoma With Increased γδ T Cells: A Potential Diagnostic Pitfall.Am J Dermatopathol. 2025 Jun 17;47(8):634-637. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0000000000002999. Am J Dermatopathol. 2025. PMID: 40532089
-
Orbital atypical lymphocytic panniculitis preceding conjunctival marginal zone lymphoma in the same patient with undifferentiated connective tissue disease: a case-based review.Rheumatol Int. 2025 Aug 13;45(9):199. doi: 10.1007/s00296-025-05944-x. Rheumatol Int. 2025. PMID: 40801975 Review.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Subcutaneous Panniculitis-Like T-Cell Lymphoma Presenting as a Targetoid Plaque in a Pediatric Patient: A Case Report and Review of Literature.Pediatr Dermatol. 2025 Jul-Aug;42(4):822-825. doi: 10.1111/pde.15873. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Pediatr Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39805581 Review.
-
A Case of Pediatric Subcutaneous Panniculitis-like T-Cell Lymphoma Successfully Treated with Immunosuppressive Therapy.Children (Basel). 2025 Aug 5;12(8):1029. doi: 10.3390/children12081029. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40868481 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

