Residual host cell proteins: sources, properties, detection methods and data acquisition modes
- PMID: 40901073
- PMCID: PMC12399514
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1658366
Residual host cell proteins: sources, properties, detection methods and data acquisition modes
Abstract
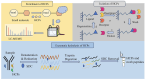
Host cell proteins (HCPs) are process-related impurities derived from host organisms used for recombinant protein production in biopharmaceutical manufacturing. The generation of HCPs may lead to potential safety risks, such as immunogenicity, reduced drug efficacy and long-term side effects. Therefore, in the biopharmaceutical process, even trace amounts of HCPs need to be strictly regulated and controlled. The main bottlenecks associated with the detection of HCPs include a wide dynamic range of detection and instability of HCPs. Due to its high sensitivity and high resolution, mass spectrometry has attracted more and more attention in HCP detection, but it still cannot completely replace enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The research in the future includes the development of more efficient sample pretreatment methods and data processing techniques to improve the sensitivity and accuracy of detection. At the same time, combined with risk assessment and process optimization, it is expected to further reduce the residual risk of HCP. This review discusses the sources, properties, pretreatment and detection of residual HCPs in therapeutic products, along with current regulatory considerations and future advancements.
Keywords: characterization; detection; host cell proteins; pretreatment; sources.
Copyright © 2025 Yao, Wen, Pan and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

