Arousal Threshold Score: A New Indicator for Examining the Relationship Between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Overlap Syndrome - A Retrospective Study
- PMID: 40901280
- PMCID: PMC12399886
- DOI: 10.2147/NSS.S551944
Arousal Threshold Score: A New Indicator for Examining the Relationship Between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Overlap Syndrome - A Retrospective Study
Abstract
Objective: A low arousal threshold (AT) appears to contribute to obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) pathogenesis. However, the role of low AT in OSA and overlap syndrome (OVS) is still unclear. This study is aimed to investigate the value of the AT score, a new method for qualifying AT, for examining the relationship between OSA and OVS, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and asthma.
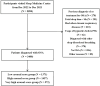
Methods: In this retrospective study, a total of 3400 adults diagnosed with OSA at a sleep medicine center were finally included. All patients were stratified into low-, high- and very high-AT score groups according to the previous logistic regression for qualifying AT. Multivariate logistic regression was conducted to evaluate the association between AT score and OVS prevalence. We compared this association with that of the apnea hypopnea index (AHI).
Results: 40.3%, 42.9% and 16.8% of OSA patients had low-, high- and very high AT score, respectively. Compared with the very high AT score, the low AT score was independently associated with the prevalence of COPD (OR = 2.17, 95% CI = 1.09-4.32) and asthma (OR = 4.54, 95% CI = 2.52-8.17). With decreasing AT score, the adjusted ORs of the comorbidities increased stepwise, particularly in some subgroups based on sex, age and BMI. Conversely, the classification of AHI did not show similar values.
Conclusion: In individuals with OSA, low AT is a common pathophysiological feature associated with COPD and asthma. The AT score is a new and effective indicator for evaluating the relationship between OSA and OVS.
Keywords: arousal threshold; asthma; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; obstructive sleep apnea; overlap syndrome; sleep-disordered breathing.
© 2025 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

