B cell depletion as a therapeutic strategy for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: rationale, evidence, and challenges
- PMID: 40901465
- PMCID: PMC12399611
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1635989
B cell depletion as a therapeutic strategy for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: rationale, evidence, and challenges
Abstract
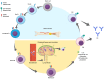
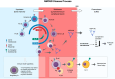
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) is a rare autoimmune disorder of the central nervous system that predominantly affects the spinal cord and optic nerves. Aquaporin-4 antibodies have been identified as a distinguishing biomarker of NMOSD, allowing for differentiation from multiple sclerosis and other mimicking neurological conditions. Targeted monoclonal antibody treatments are evolving based on an improved understanding of the pathophysiology underlying NMOSD. Of particular influence is the idea that NMOSD is an autoantibody-mediated disease involving B cells. The hope is that targeted treatments will improve not only outcomes but also the impact and burden of the disease on patients. This review summarizes the latest evidence for B cell pathophysiology in NMOSD and highlights the cellular and molecular mechanisms of B cell-driven disease. Finally, we focus on the mechanisms of action of B cell-targeted therapies as they relate to the mechanisms of disease.
Keywords: B cells; disease mechanisms; mechanism of action; neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder; pathophysiology; therapeutic targets.
Copyright © 2025 Ochi, Nakamura and Nakahara.
Conflict of interest statement
HO has served on scientific advisory boards for Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc., Biogen Japan Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, and Novartis Pharma K.K.; and has received speaker honoraria from Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc., Argenx, Biogen Japan Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Daiichi-Sankyo Co. Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Nihon Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K., Takeda Pharmaceuticals, and UCB Japan Co. Ltd. SN is an employee of Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation. JN has received honoraria from Abbvie, Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc., Astellas Pharma, Biogen Japan Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., CSL Behring, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai Co. Ltd., Fujimoto Pharma, JB Pharma, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Novartis Pharma K.K., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Sanofi, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, and Takeda Pharmaceuticals; has served on advisory boards for Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc., Biogen Japan Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Novartis Pharma K.K., and Sanofi; has received research grants from Biogen Japan Ltd. and Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.; has received research scholarships from Abbvie, Böehringer-Ingelheim, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Daiichi-Sankyo, Eisai Co. Ltd., Eli Lilly, JB Pharma, Kyowa Kirin Co. Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, MSD, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Pfizer, Shionogi & Co. Ltd., Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, and Tsumura Corporation; has received clinical trial support from Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc., Argenx, Biogen Japan Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., GSK, Novartis Pharma K.K., and Sanofi. The authors declare that this study received funding from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation for the preparation and submission of the manuscript. The funder was involved in the review of this article and the decision to submit it for publication.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

