Imaging insights into pediatric liver masses: A comprehensive minireview for hepatology practice
- PMID: 40901586
- PMCID: PMC12400384
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i8.107041
Imaging insights into pediatric liver masses: A comprehensive minireview for hepatology practice
Abstract
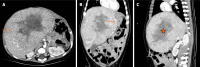
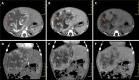
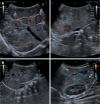
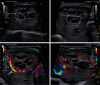
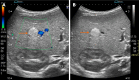
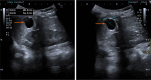
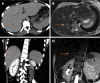
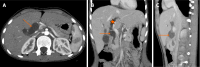
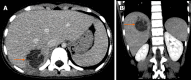
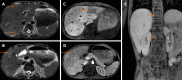
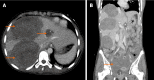
Pediatric liver masses encompass a diverse spectrum of benign and malignant lesions, with distinct patterns based on patient age. Optimal imaging is critical for timely diagnosis, management, and prognosis. This pictorial minireview categorizes pediatric liver masses by age group to guide hepatology and radiology practice, with an emphasis on imaging characteristics. In children from birth to six years of age, the most common liver masses include hepatoblastoma, the most common primary hepatic malignancy in this age group; infantile hemangioma, a benign vascular tumor with a characteristic appearance on imaging; and mesenchymal hamartoma, a rare developmental lesion. For children older than six years, liver masses are distinct, with hepatocellular carcinoma being the predominant malignant lesion. Benign masses such as focal nodular hyperplasia and hepatocellular adenoma also emerge in this age range, often linked to hormonal influences or metabolic disorders. The masses observed across all pediatric age groups include hepatic cysts, choledochal cysts, hydatid cysts, pyogenic and amebic abscesses, tuberculosis, lymphoma, and metastases, each presenting with unique imaging features essential for differential diagnosis. This minireview provides a comprehensive, age-based overview of pediatric liver masses, focusing on clinical presentation and key imaging findings to support accurate diagnosis and optimize management strategies in clinical hepatology, particularly in low resource settings.
Keywords: Benign liver lesions; Hepatic masses; Malignant liver lesions; Pediatric hepatic imaging; Pediatric liver tumors.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this article.
Figures













Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Elbow Fractures Overview.2025 Jul 7. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 7. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 28723005 Free Books & Documents.
-
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome.2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31613449 Free Books & Documents.
-
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound using SonoVue® (sulphur hexafluoride microbubbles) compared with contrast-enhanced computed tomography and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the characterisation of focal liver lesions and detection of liver metastases: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2013 Apr;17(16):1-243. doi: 10.3310/hta17160. Health Technol Assess. 2013. PMID: 23611316 Free PMC article.
-
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome.2000 Mar 3 [updated 2023 Sep 21]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. 2000 Mar 3 [updated 2023 Sep 21]. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, Pagon RA, Wallace SE, Amemiya A, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993–2025. PMID: 20301568 Free Books & Documents. Review.
References
-
- Towbin AJ, Meyers RL, Woodley H, Miyazaki O, Weldon CB, Morland B, Hiyama E, Czauderna P, Roebuck DJ, Tiao GM. 2017 PRETEXT: radiologic staging system for primary hepatic malignancies of childhood revised for the Paediatric Hepatic International Tumour Trial (PHITT) Pediatr Radiol. 2018;48:536–554. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

