Galectin-3 induces neurodevelopmental apical-basal polarity and regulates gyrification
- PMID: 40901969
- PMCID: PMC12407091
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adt5859
Galectin-3 induces neurodevelopmental apical-basal polarity and regulates gyrification
Abstract
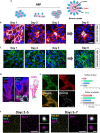
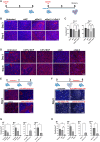
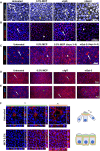
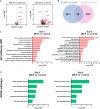
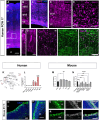
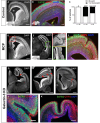
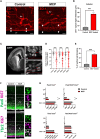
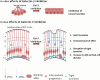
Apical-basal polarity (ABP) establishment and maintenance is necessary for proper brain development, yet how it is controlled is unclear. Galectin-3 (Gal-3) has been previously implicated in ABP of epithelial cells, and, here, we find that it is apically expressed in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) during neural induction. Gal-3 blockade disrupts ABP and alters the distribution of junctional proteins in hESC-derived neural rosettes and is rescued by addition of recombinant Gal-3. Transcriptomics analysis shows that blocking Gal-3 regulates expression of genes responsible for nervous system development and cell junction assembly, among others. Last, Gal-3 blockade during embryonic development in vivo reduces horizontal cell divisions, disturbs cortical layering of neural progenitors, and induces gyrification. These data uncover a regulatory mechanism for ABP in the brain and warrant caution in modulating Gal-3 during pregnancy.
Figures
References
-
- Buckley C. E., St Johnston D., Apical-basal polarity and the control of epithelial form and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 23, 559–577 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Fietz S. A., Huttner W. B., Cortical progenitor expansion, self-renewal and neurogenesis-a polarized perspective. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 21, 23–35 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Del-Valle-Anton L., Borrell V., Folding brains: From development to disease modeling. Physiol. Rev. 102, 511–550 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Hevner R. F., From radial glia to pyramidal-projection neuron: Transcription factor cascades in cerebral cortex development. Mol. Neurobiol. 33, 33–50 (2006). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

