Characteristics and management of mechanically ventilated patients in South Korea compared with other high-income Asian countries and regions
- PMID: 40903405
- PMCID: PMC12408485
- DOI: 10.4266/acc.003336
Characteristics and management of mechanically ventilated patients in South Korea compared with other high-income Asian countries and regions
Abstract
Background: This study investigated the characteristics of mechanically ventilated patients in South Korean intensive care units (ICUs).
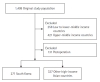
Methods: We conducted a subgroup analysis of a multinational observational study. Data from 271 mechanically ventilated patients in South Korean ICUs were analyzed for demographics, ventilation practices, and mortality, and were compared with those of 327 patients from other high-income Asian countries.
Results: South Korean patients were older (mean age: 67 vs. 62 years, P<0.001) and had lower ratio of the partial pressure of arterial oxygen to the fraction of inspired oxygen (255.5 vs. 306.2, P<0.001). South Korean ICUs exhibited higher patient-to-nurse ratios (2.6 vs. 1.9, P<0.001) and more beds per unit (20.5 vs. 16.0, P=0.017). The use of sufficient positive end-expiratory pressure for patients (PEEP) for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) was less frequent in South Korea (62.2% vs. 91.2%, P=0.005). Mortality rates were similar between South Korean patients and those in other high-income Asian countries (38.0% vs. 34.2%, P=0.401). Significant mortality predictors in South Korea included age ≥65 years (odds ratio [OR], 4.03; P=0.039) and a Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score ≥8 (OR, 2.36; P=0.031). The presence of respiratory therapists was associated with reduced mortality (OR, 0.52; P=0.034).
Conclusions: Despite higher age and patient-to-nurse ratios in South Korean ICUs, outcomes were comparable to those in other high-income Asian countries. The suboptimal use of sufficient PEEP with ARDS indicates potential areas for improvement. Additionally, the beneficial impact of respiratory therapists on mortality rates warrants further investigation.
Keywords: Asia; Korea; artificial respiration; intensive care unit; ventilator-induced lung injury.
Conflict of interest statement
Kwangha Lee and Woo Hyun Cho are editorial board members of the journal but were not involved in the peer reviewer selection, evaluation, or decision process of this article. No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Positioning for acute respiratory distress in hospitalised infants and children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jun 6;6(6):CD003645. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003645.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35661343 Free PMC article.
-
High versus low positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) levels for mechanically ventilated adult patients with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jun 6;2013(6):CD009098. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009098.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 30;3:CD009098. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009098.pub3. PMID: 23740697 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Prone position for acute respiratory failure in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 13;2015(11):CD008095. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008095.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26561745 Free PMC article.
-
Ventilator Management(Archived).2023 Mar 27. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Mar 27. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 28846232 Free Books & Documents.
-
Music interventions for mechanically ventilated patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;2014(12):CD006902. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006902.pub3. Epub 2014 Dec 9. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 25490233 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources